Science: ideas and frameworks explained
A collection of ideas, frameworks and techniques related to Science, explained clearly so they are easy to understand and share. Browse practical concepts, principles and tips, with visual examples to make them memorable.
 The Volcanic Explosivity Index (VEI): Comparing Eruptions
The Volcanic Explosivity Index (VEI): Comparing Eruptions Laplace's Demon
Laplace's Demon Dune Types: Transverse, Linear, Barchan, Star Dunes
Dune Types: Transverse, Linear, Barchan, Star Dunes Mirage: why do we see a pool of water?
Mirage: why do we see a pool of water?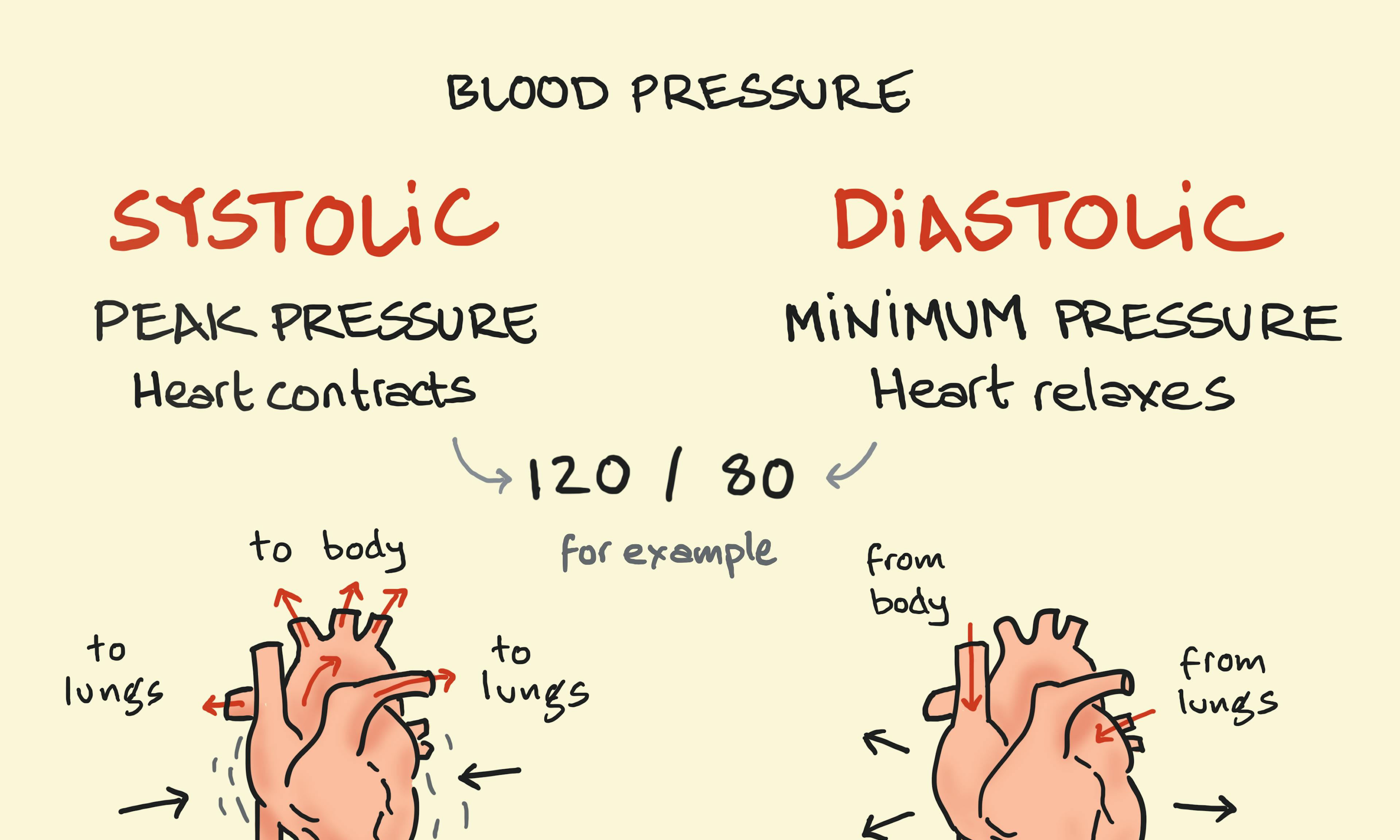 Systolic and Diastolic Blood Pressure
Systolic and Diastolic Blood Pressure Science and Engineering: What’s the Difference?
Science and Engineering: What’s the Difference?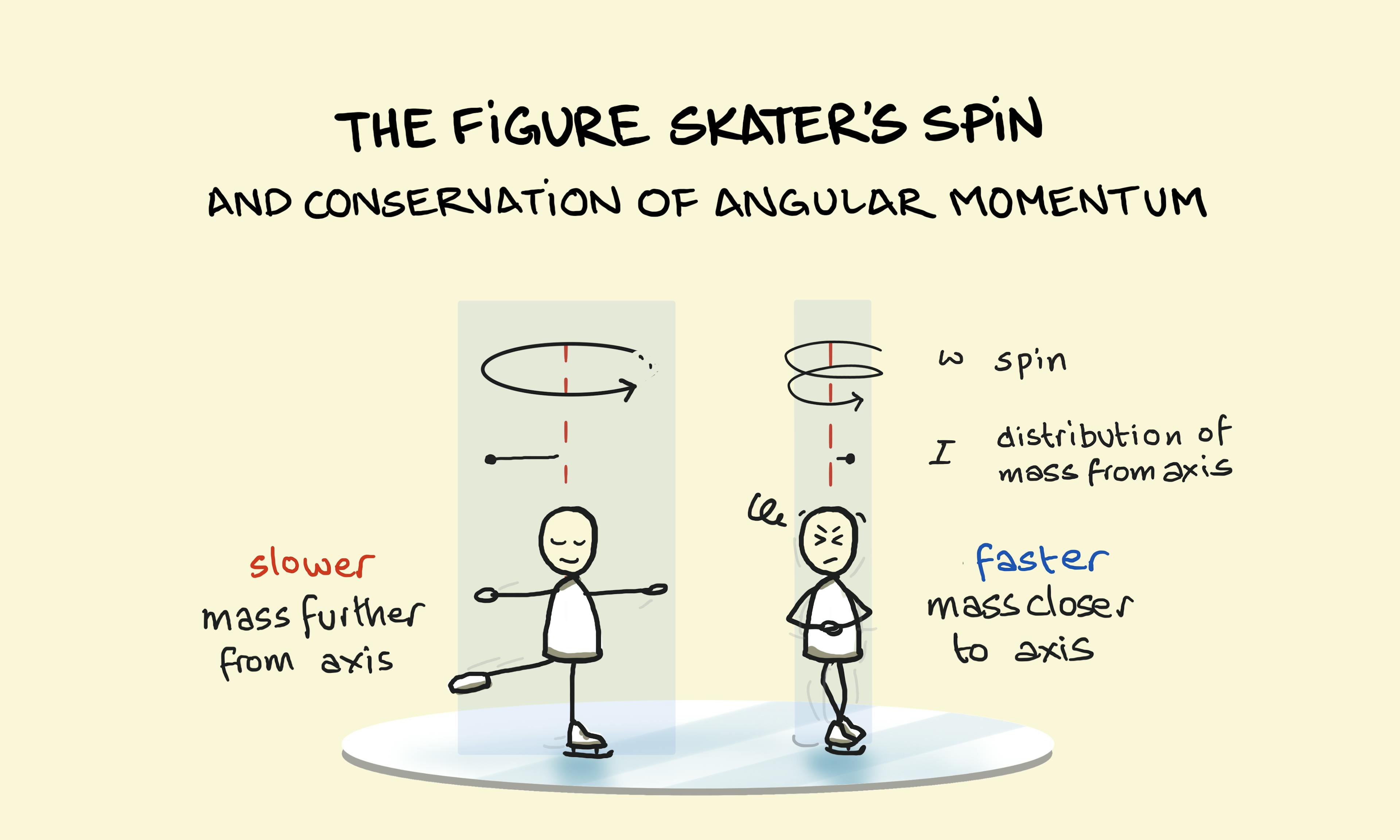 The Figure Skater's Spin and the Conservation of Angular Momentum
The Figure Skater's Spin and the Conservation of Angular Momentum Temperature Palindromes: Converting Between Fahrenheit and Celsius
Temperature Palindromes: Converting Between Fahrenheit and Celsius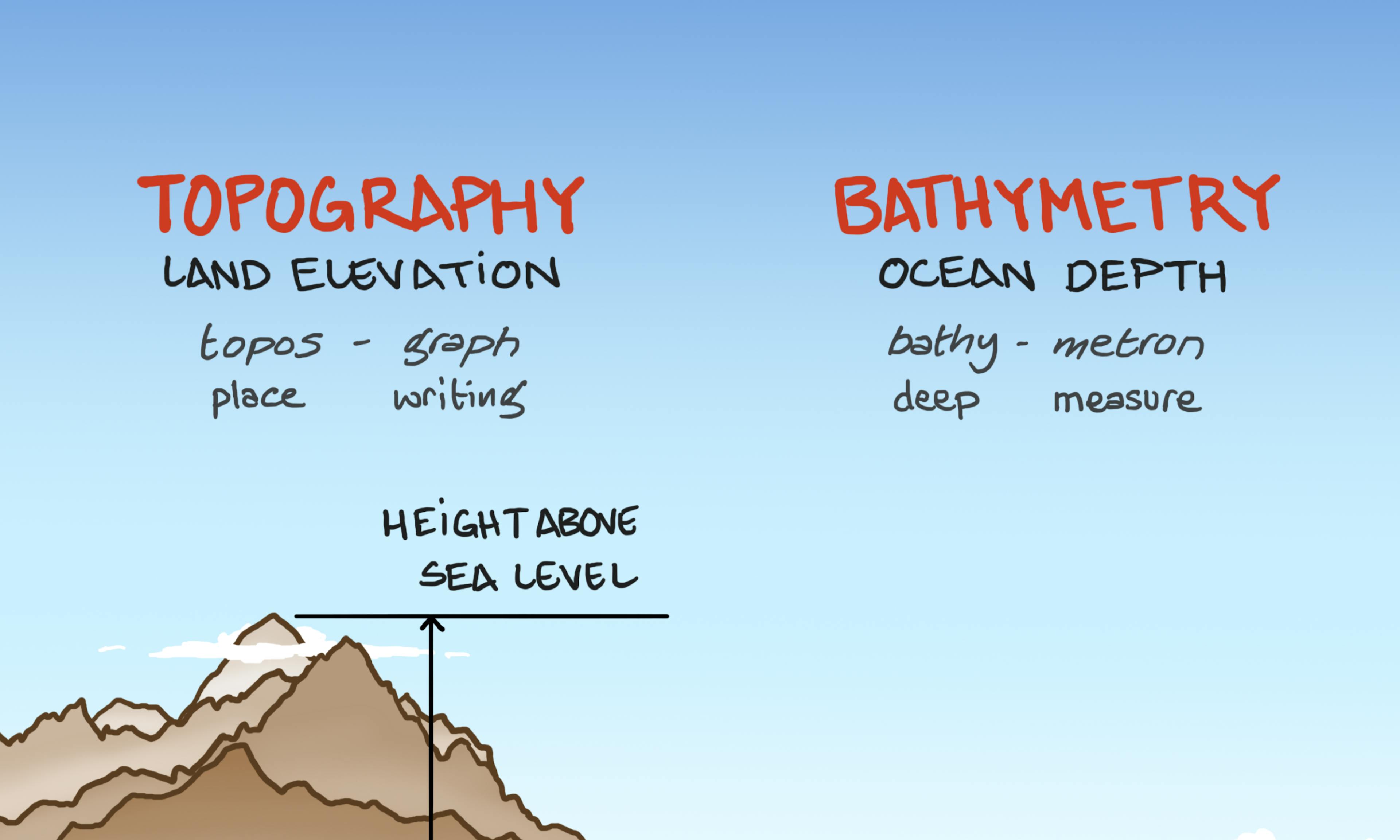 Topography and Bathymetry
Topography and Bathymetry Looking Back in Time: The Speed of Light and the Night Sky
Looking Back in Time: The Speed of Light and the Night Sky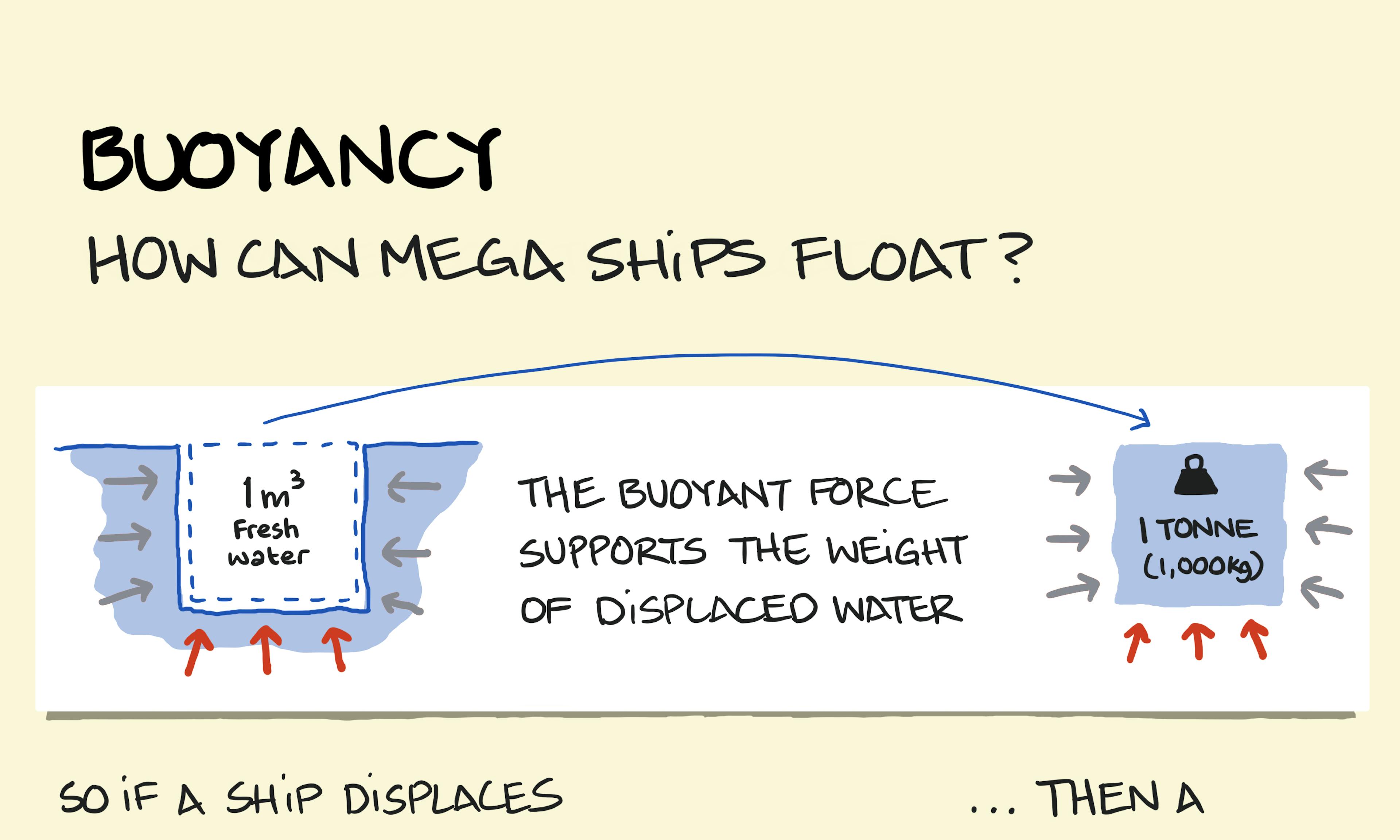 Buoyancy
Buoyancy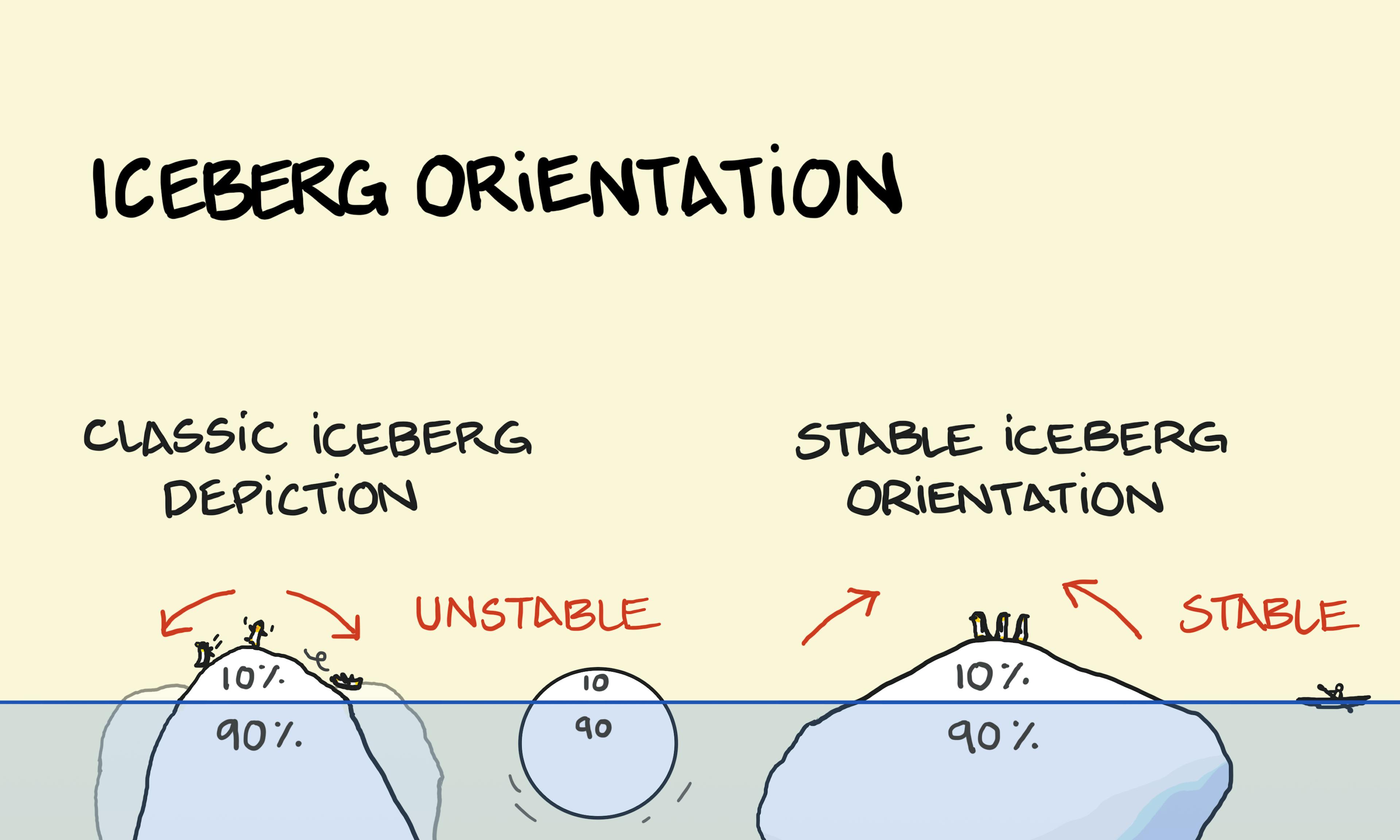 Iceberg orientation
Iceberg orientation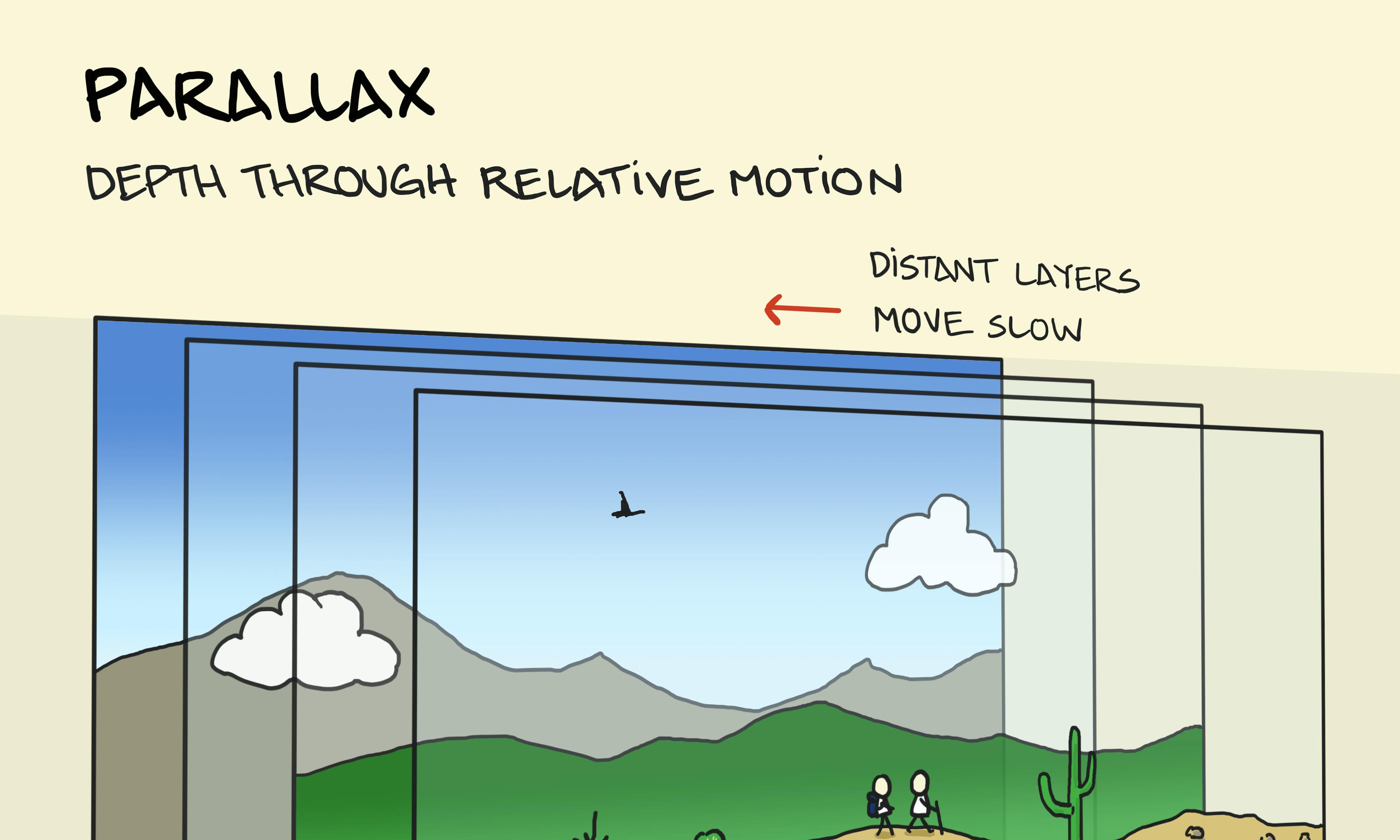 Parallax
Parallax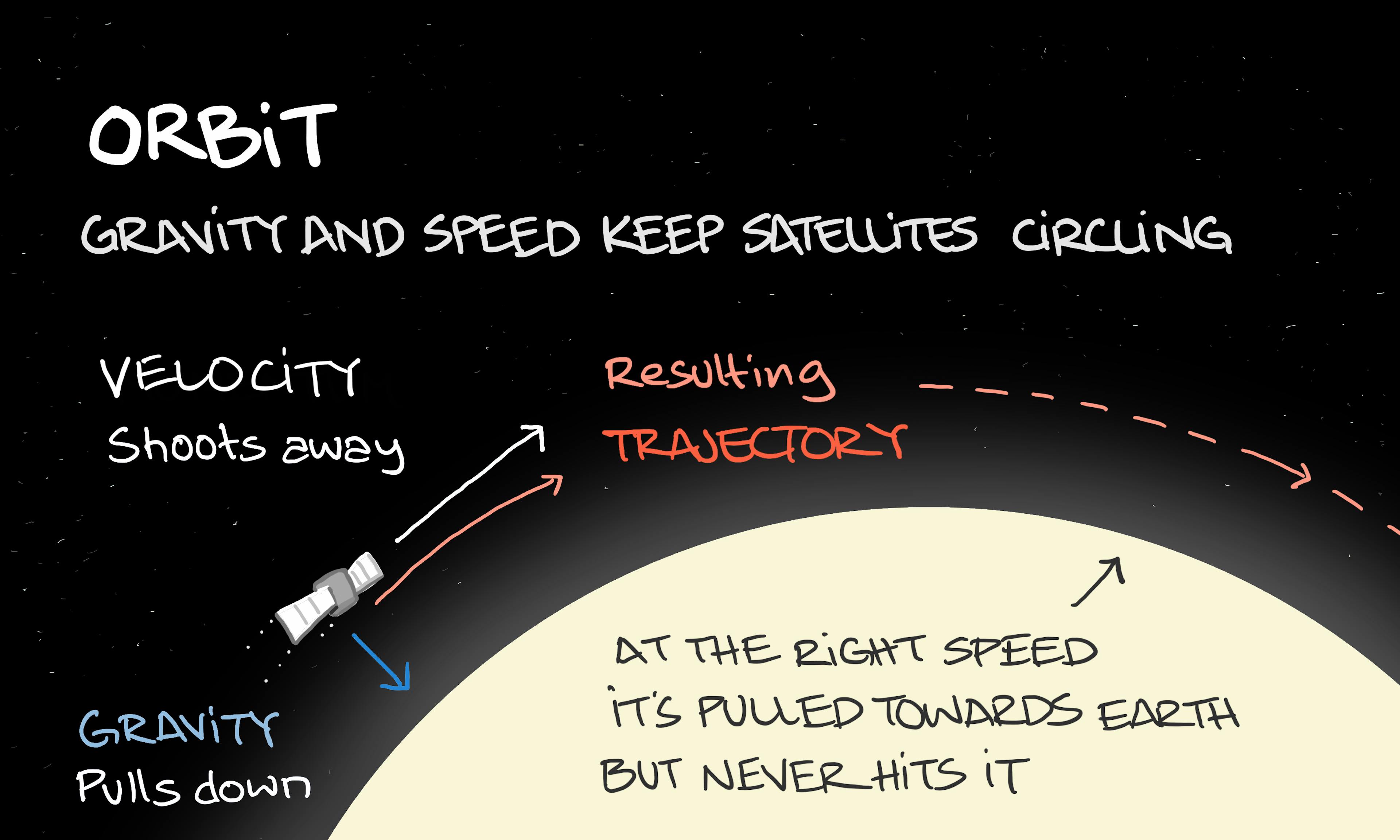 Orbit
Orbit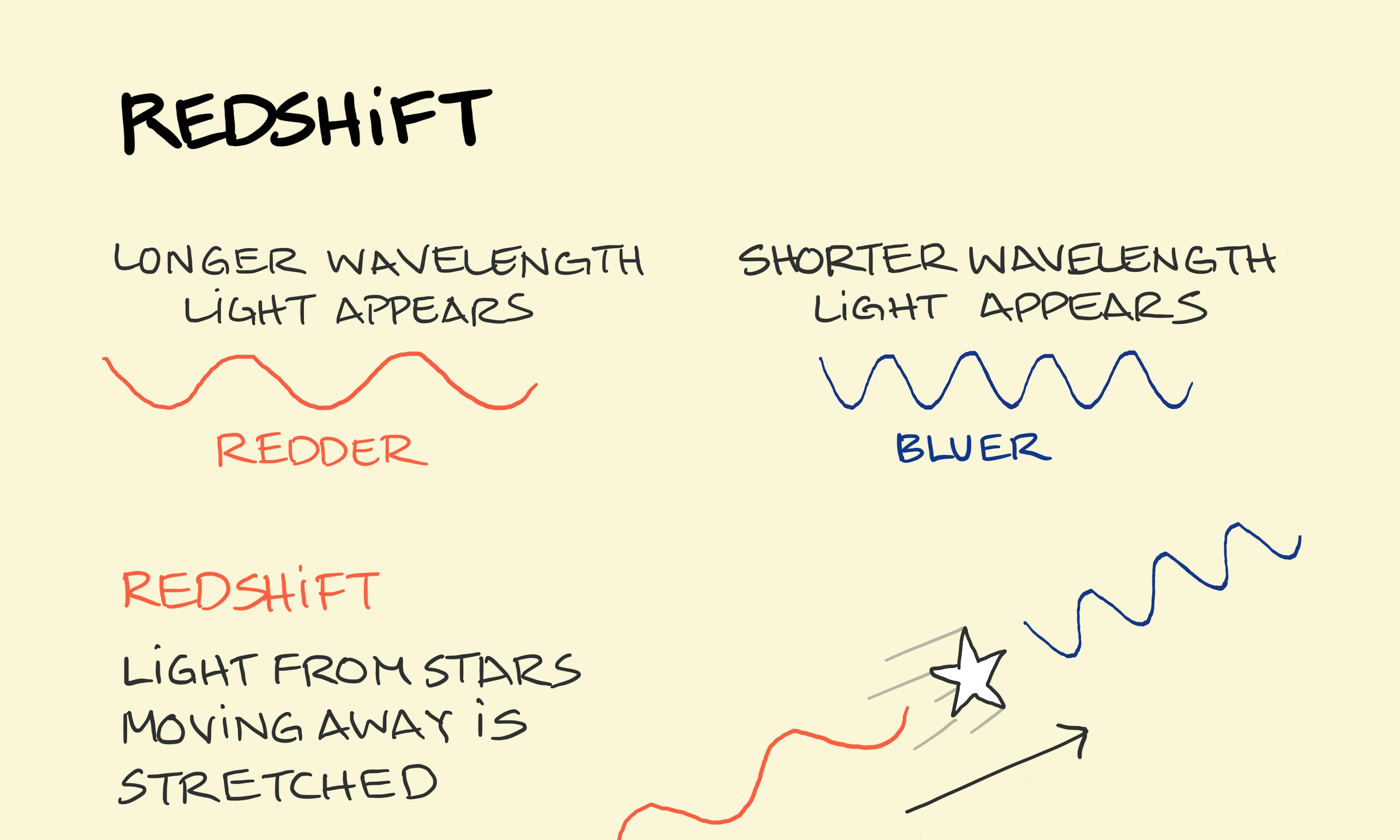 Redshift
Redshift Physics Envy
Physics Envy Brilliance bias
Brilliance bias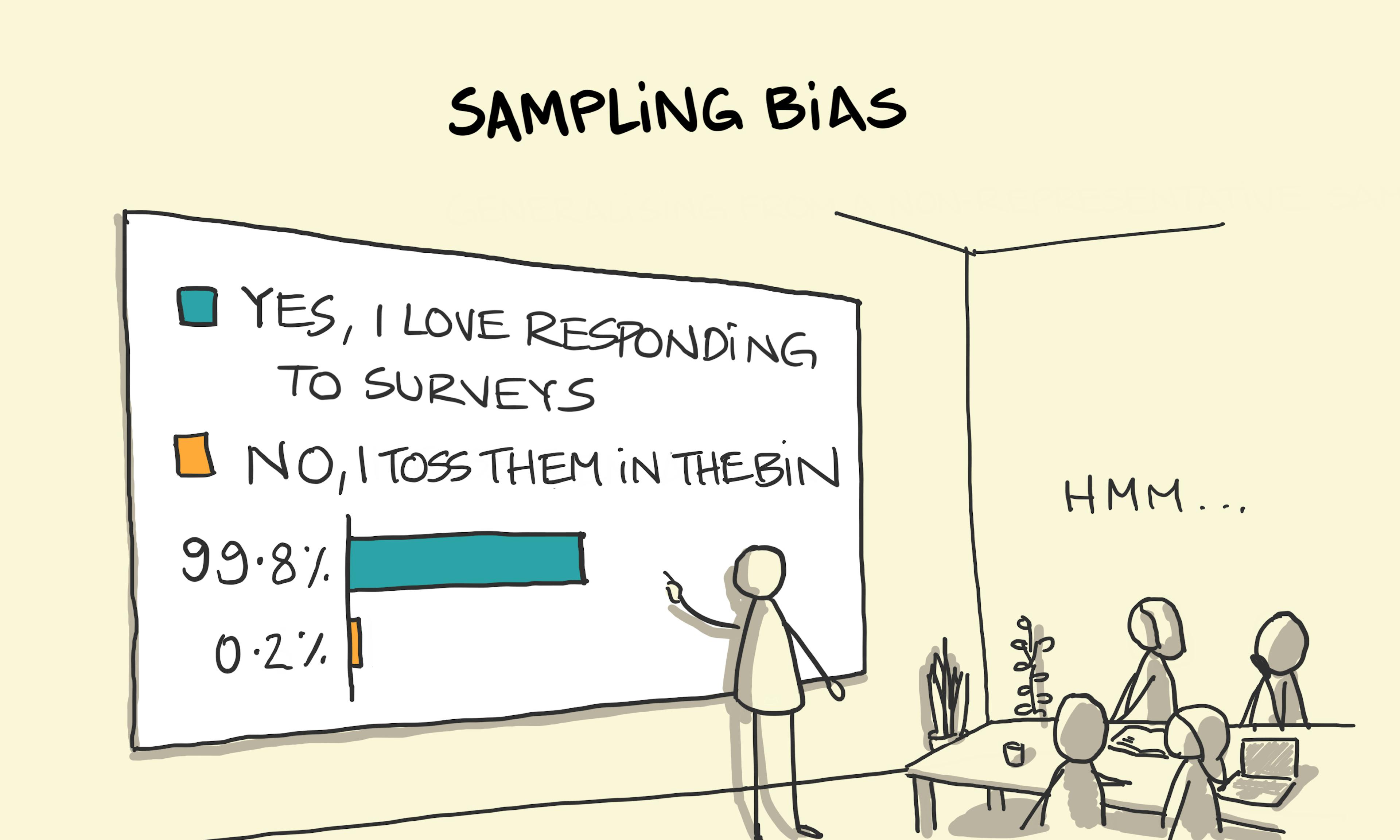 Sampling bias
Sampling bias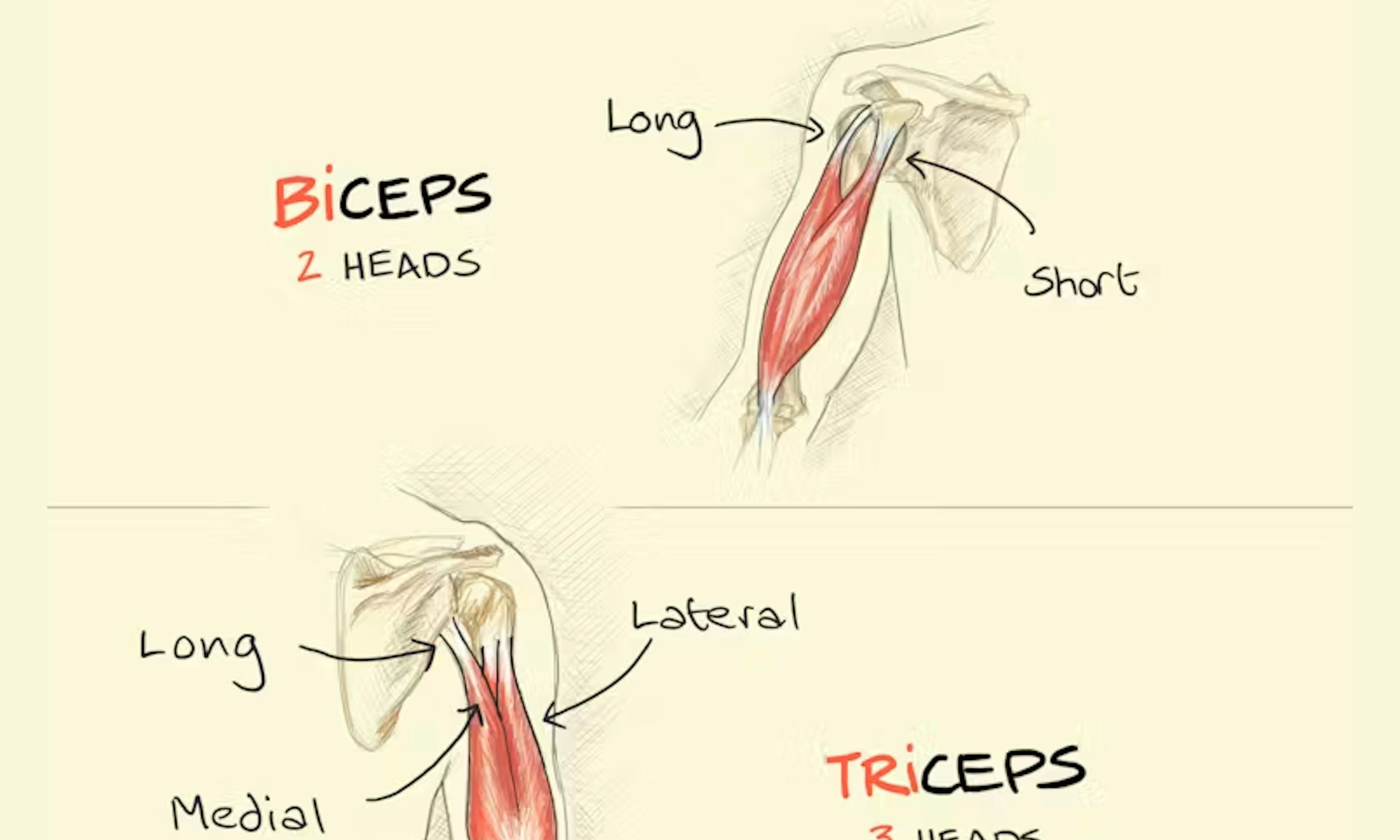 Biceps, Triceps, Quadriceps: Meaning and Difference
Biceps, Triceps, Quadriceps: Meaning and Difference You get what you measure
You get what you measure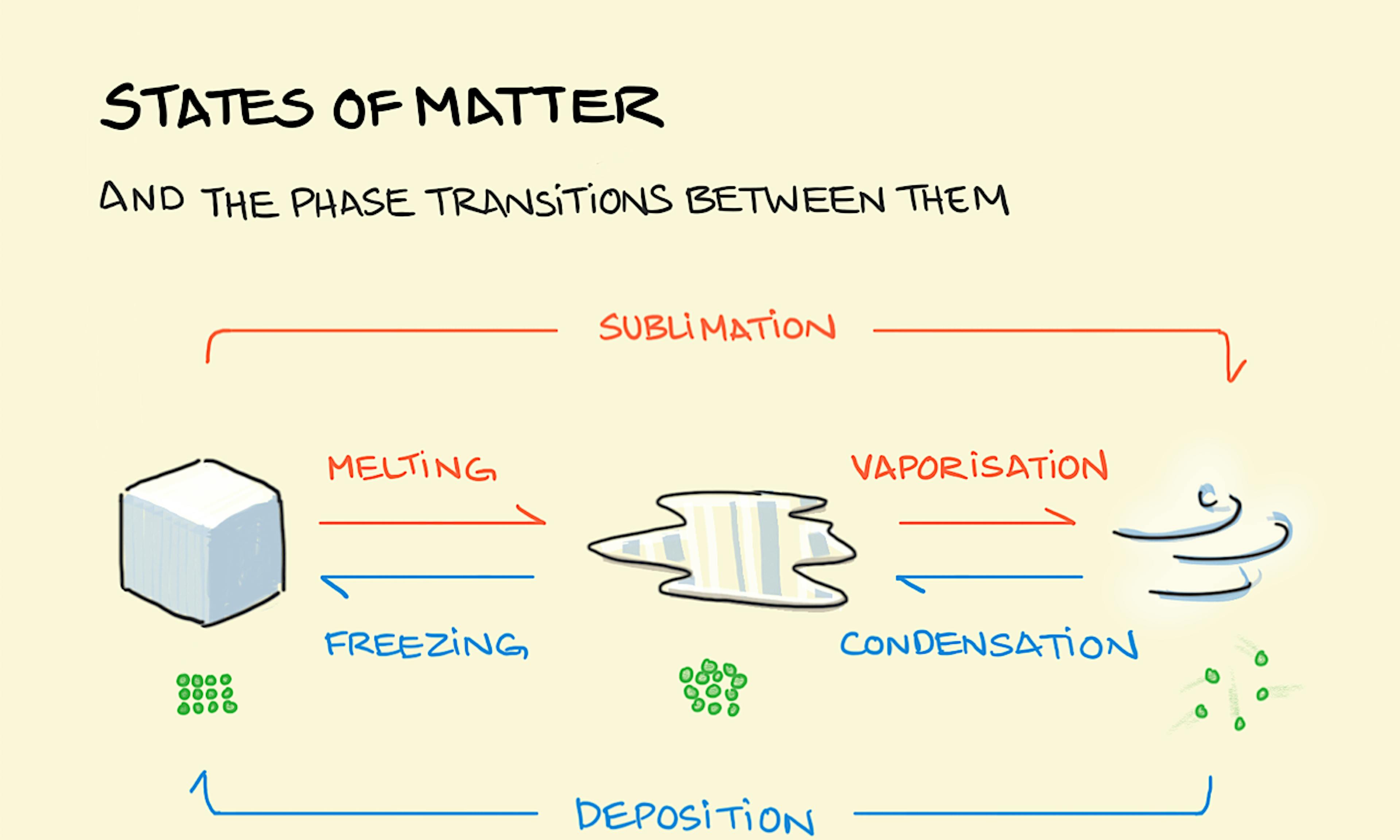 States of matter
States of matter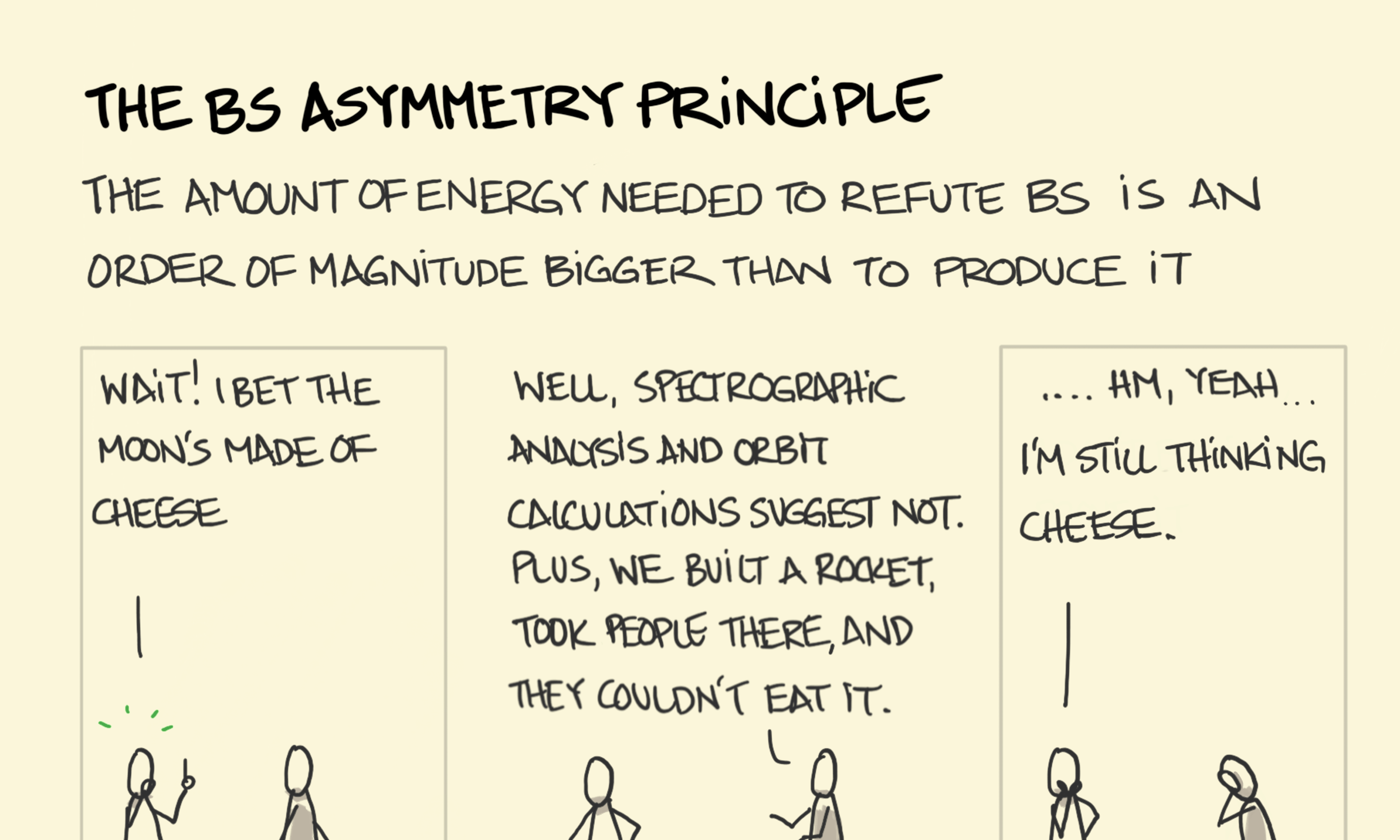 The BS asymmetry principle
The BS asymmetry principle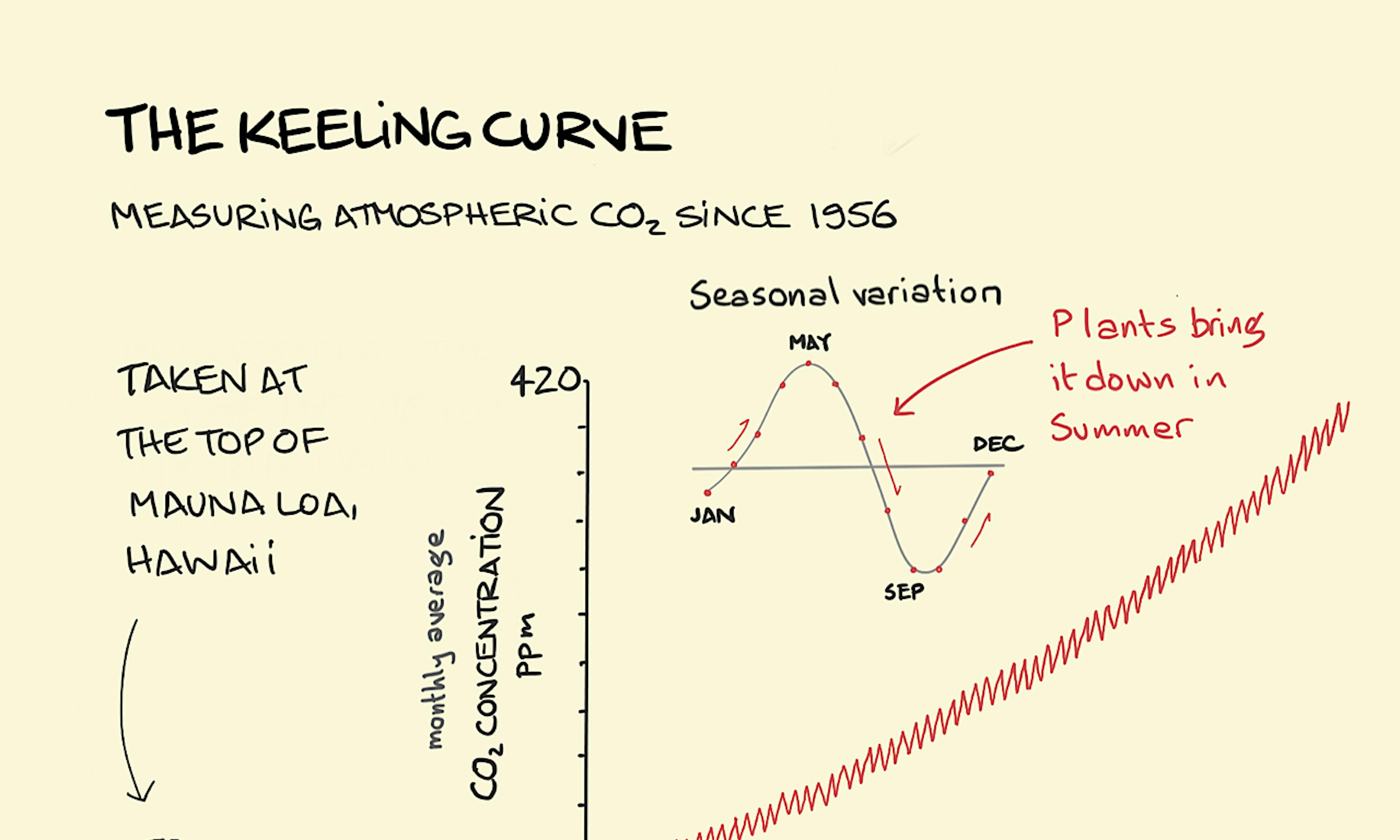 The Keeling curve
The Keeling curve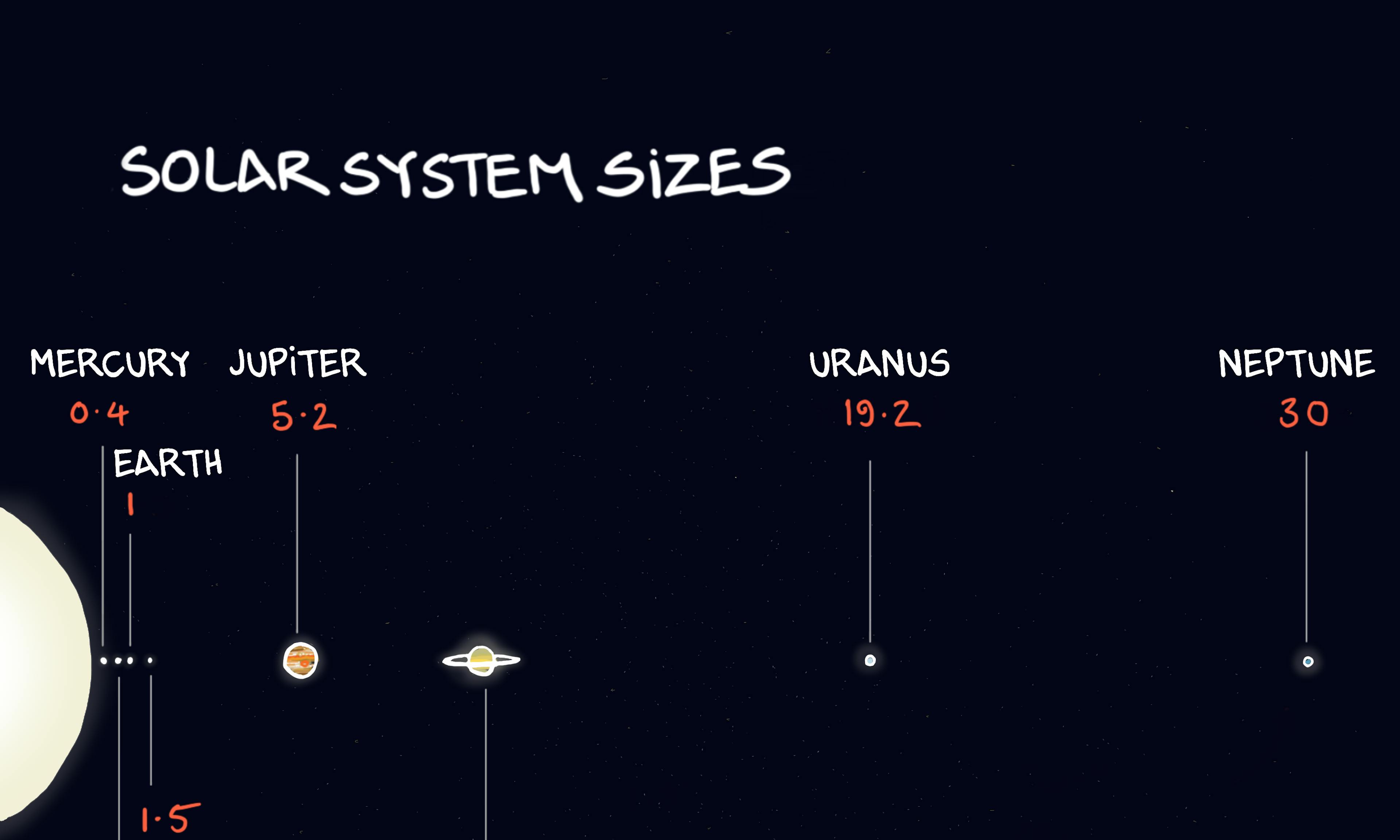 Solar system planets: how big is the solar system?
Solar system planets: how big is the solar system?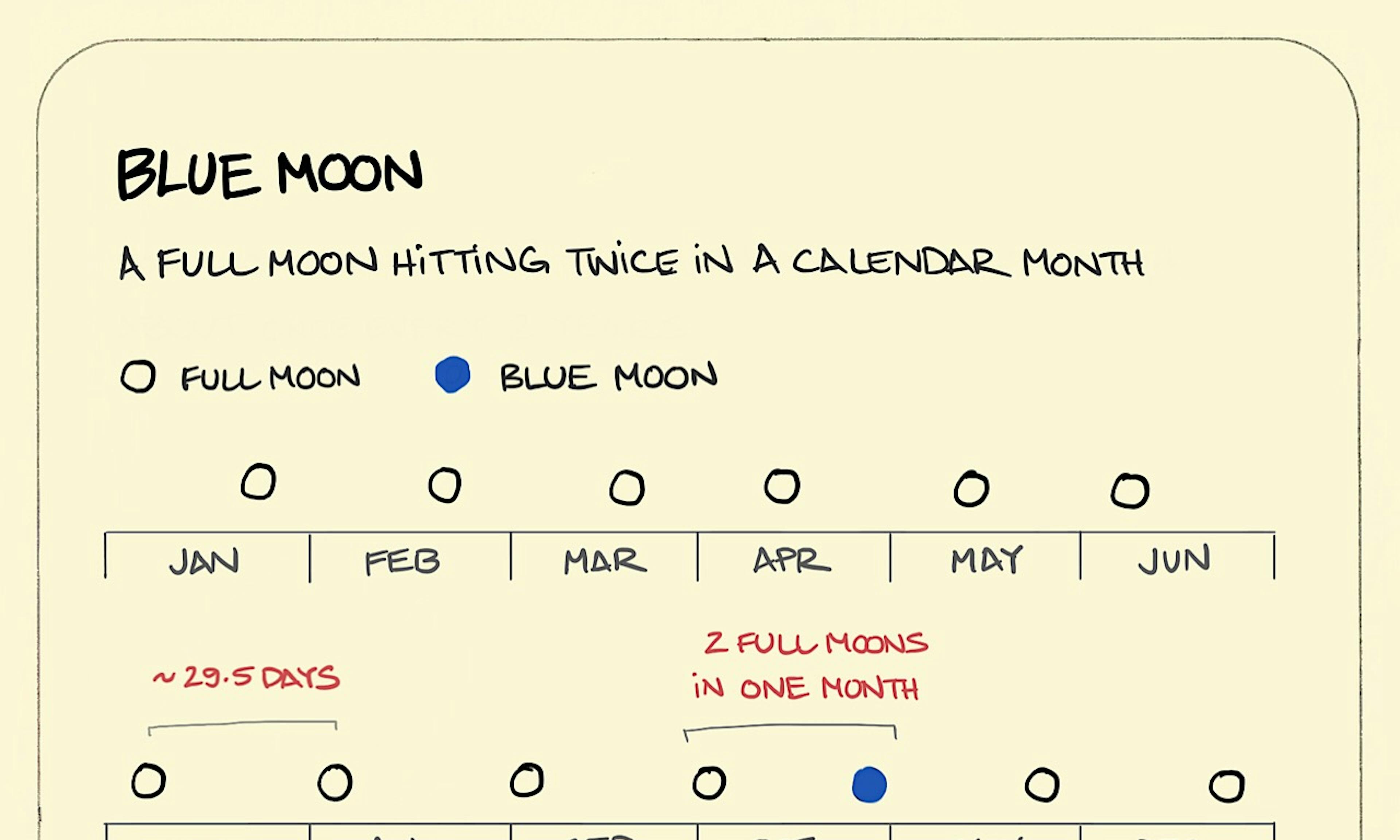 What is a blue moon?
What is a blue moon?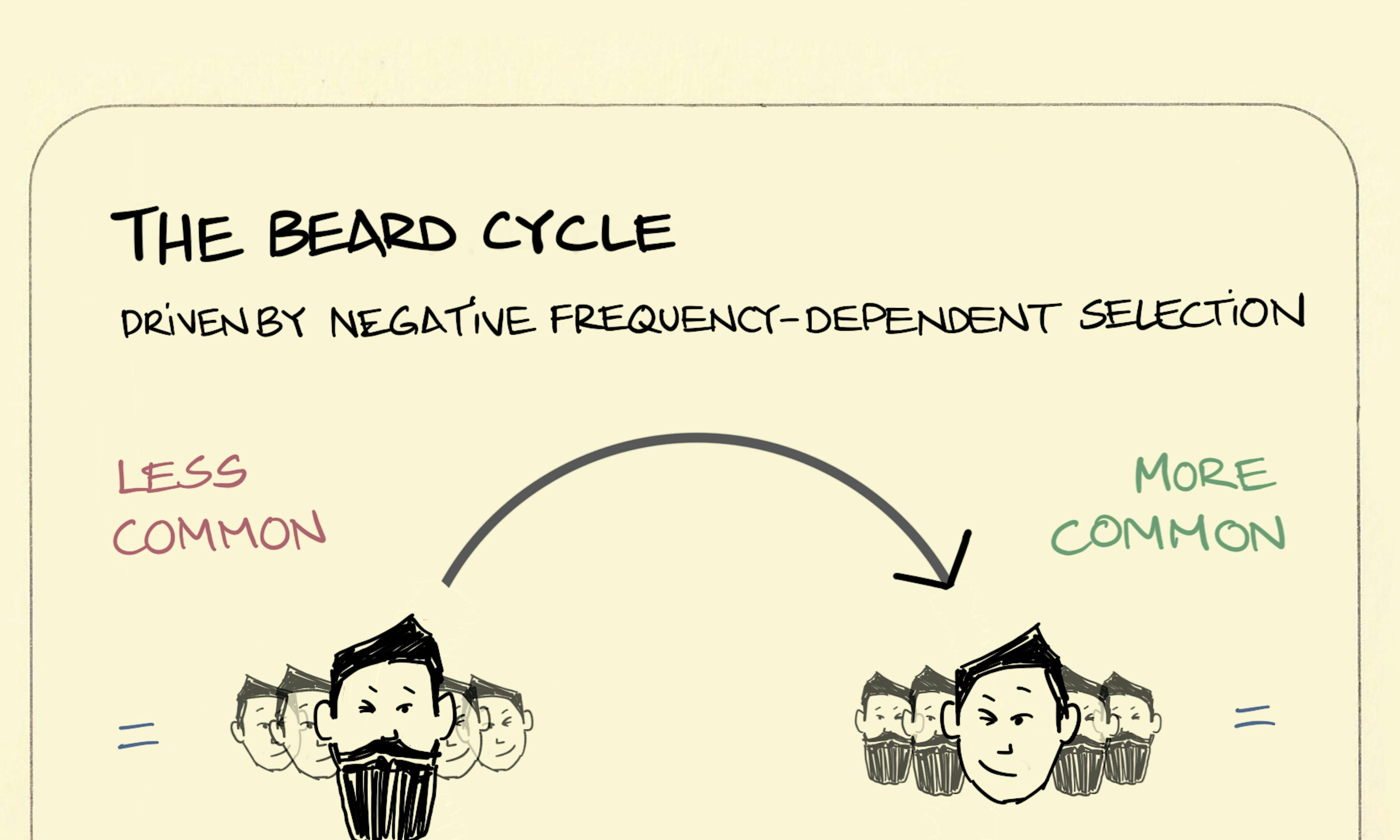 The beard cycle
The beard cycle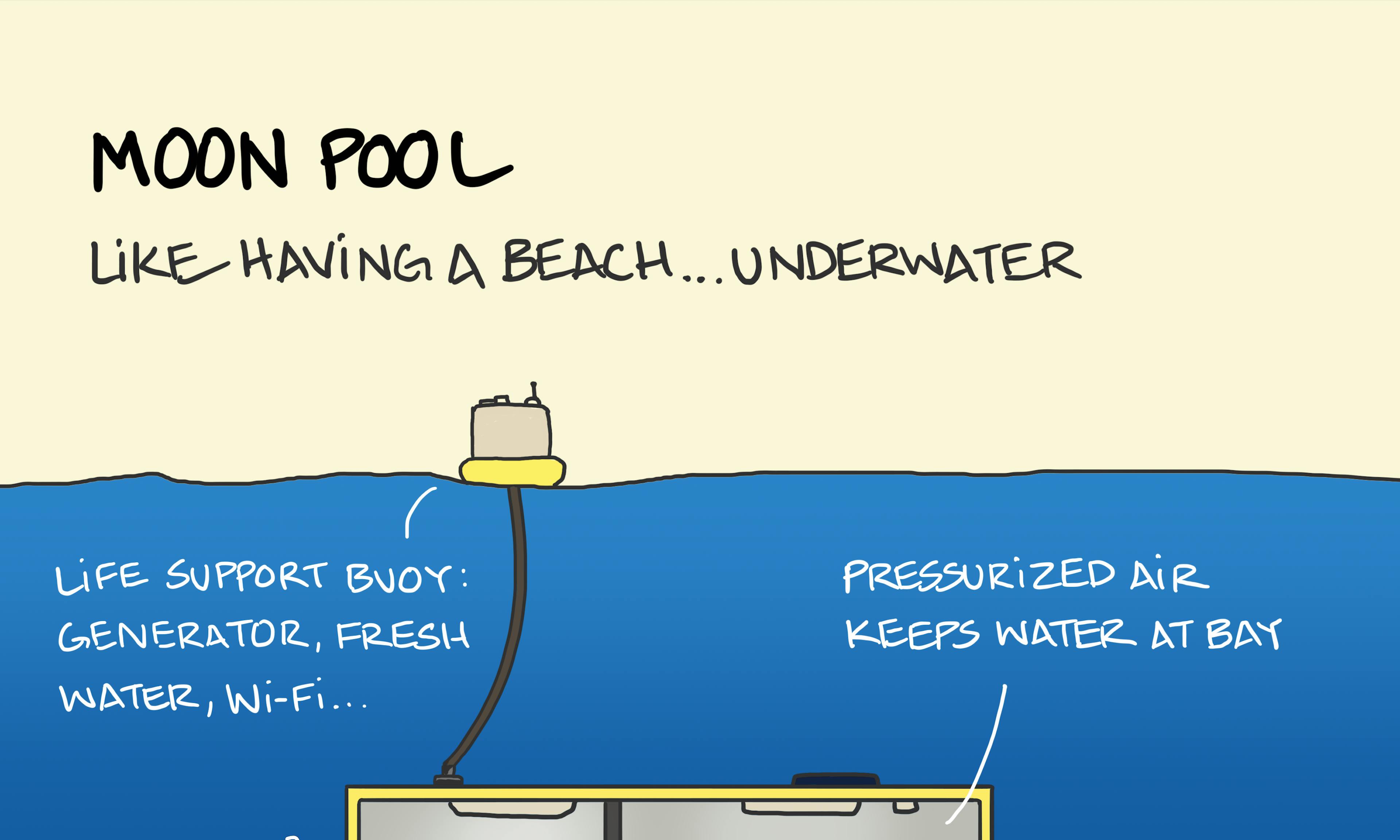 Moon pool
Moon pool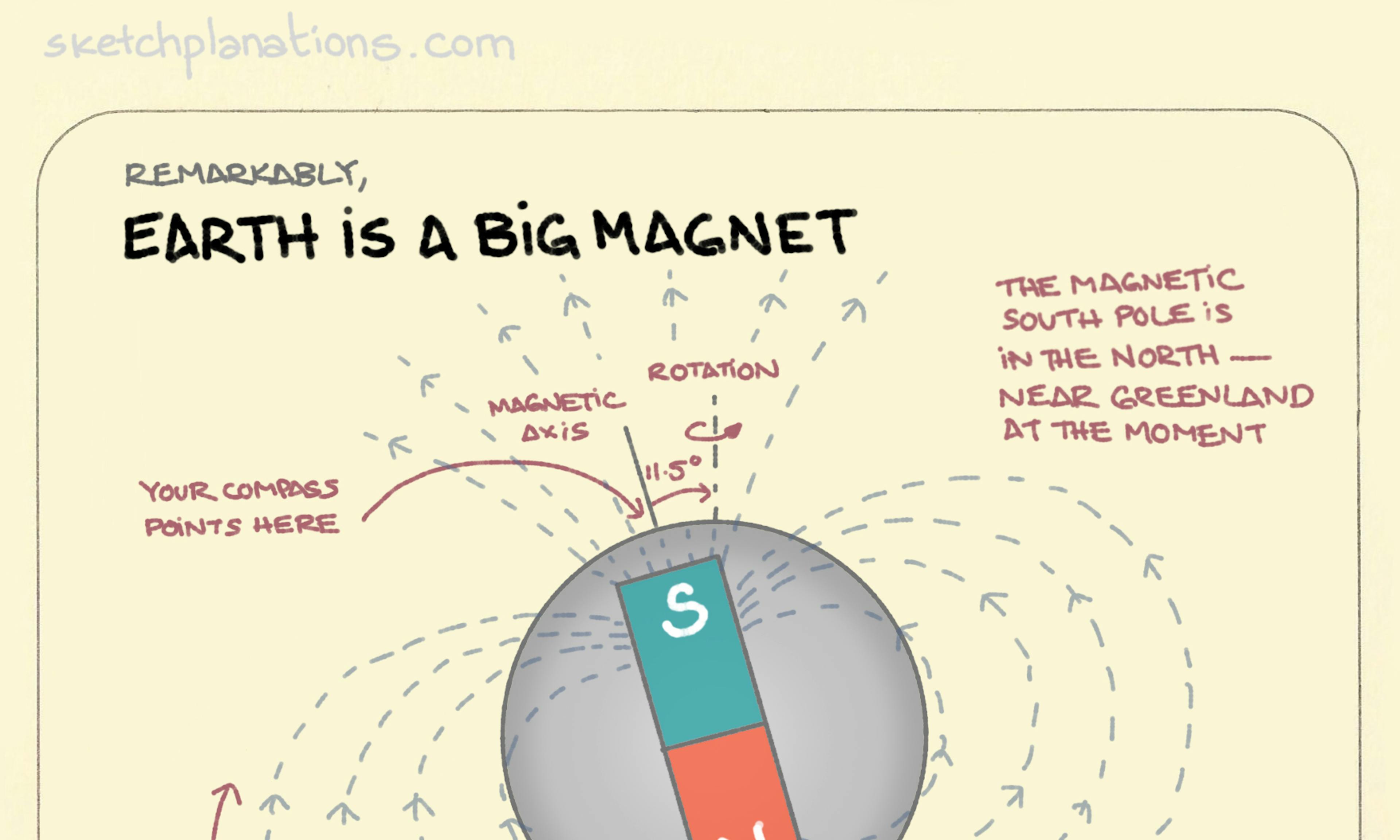 Earth is a big magnet.
Earth is a big magnet.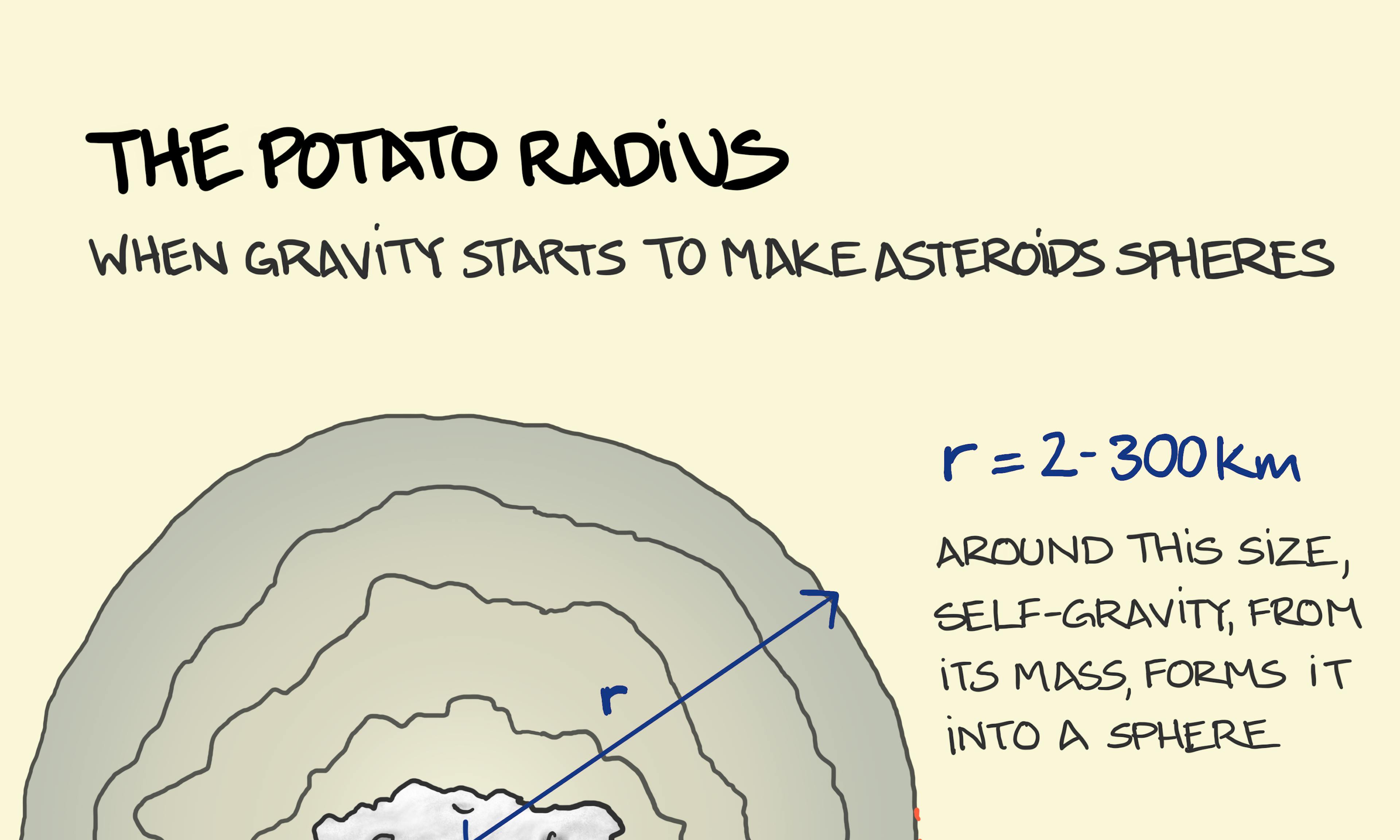 The Potato Radius: When Asteroids Turn Spherical
The Potato Radius: When Asteroids Turn Spherical Stalactites, Stalagmites
Stalactites, Stalagmites Bortle Scale
Bortle Scale Animals that regenerate
Animals that regenerate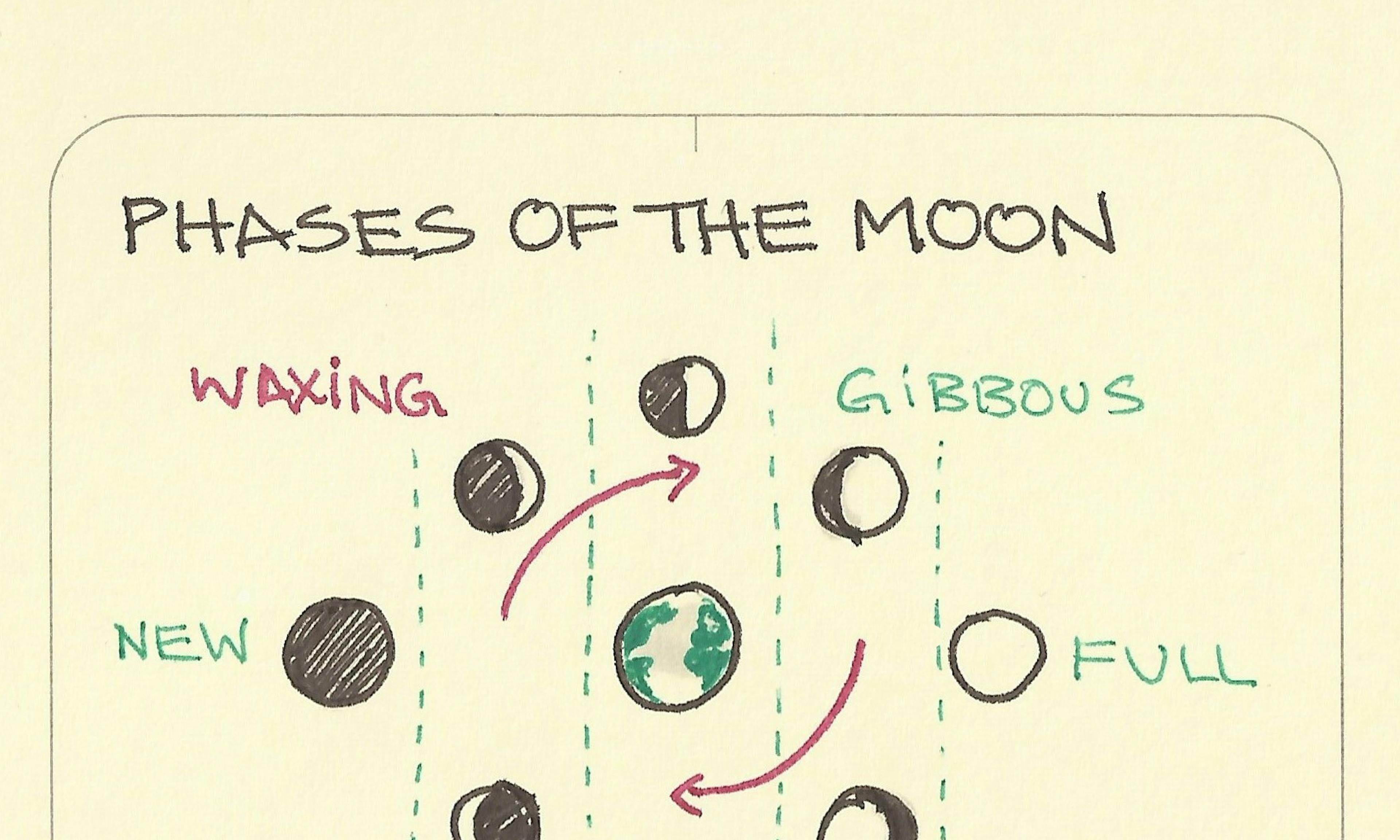 Phases of the moon
Phases of the moon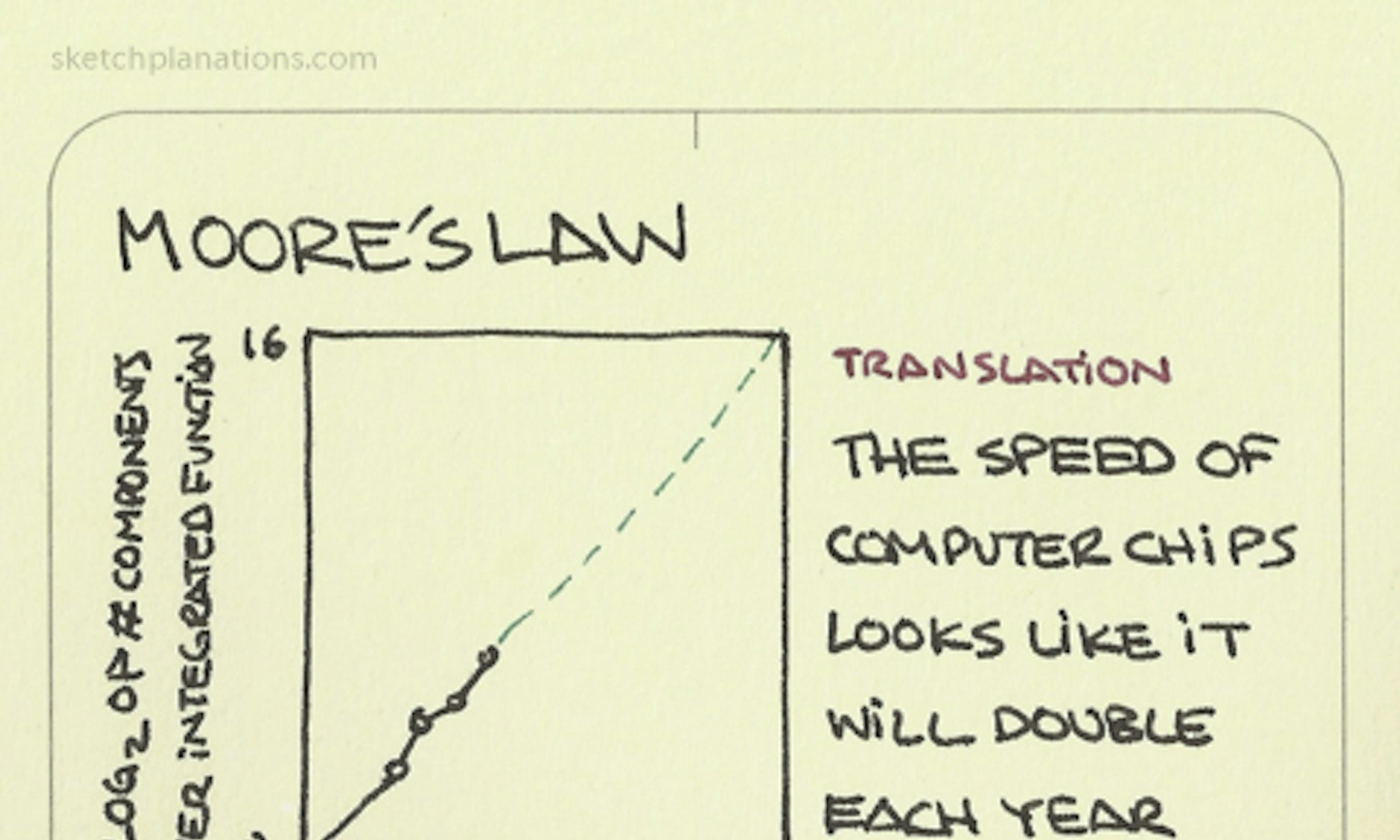 Moore’s Law
Moore’s Law How to tell a centipede from a millipede
How to tell a centipede from a millipede Asteroids, meteors and meteorites
Asteroids, meteors and meteorites Sleepy foods
Sleepy foods The Plimsoll line
The Plimsoll line Thunder clouds
Thunder clouds Darwin’s 5 principles of Natural Selection
Darwin’s 5 principles of Natural Selection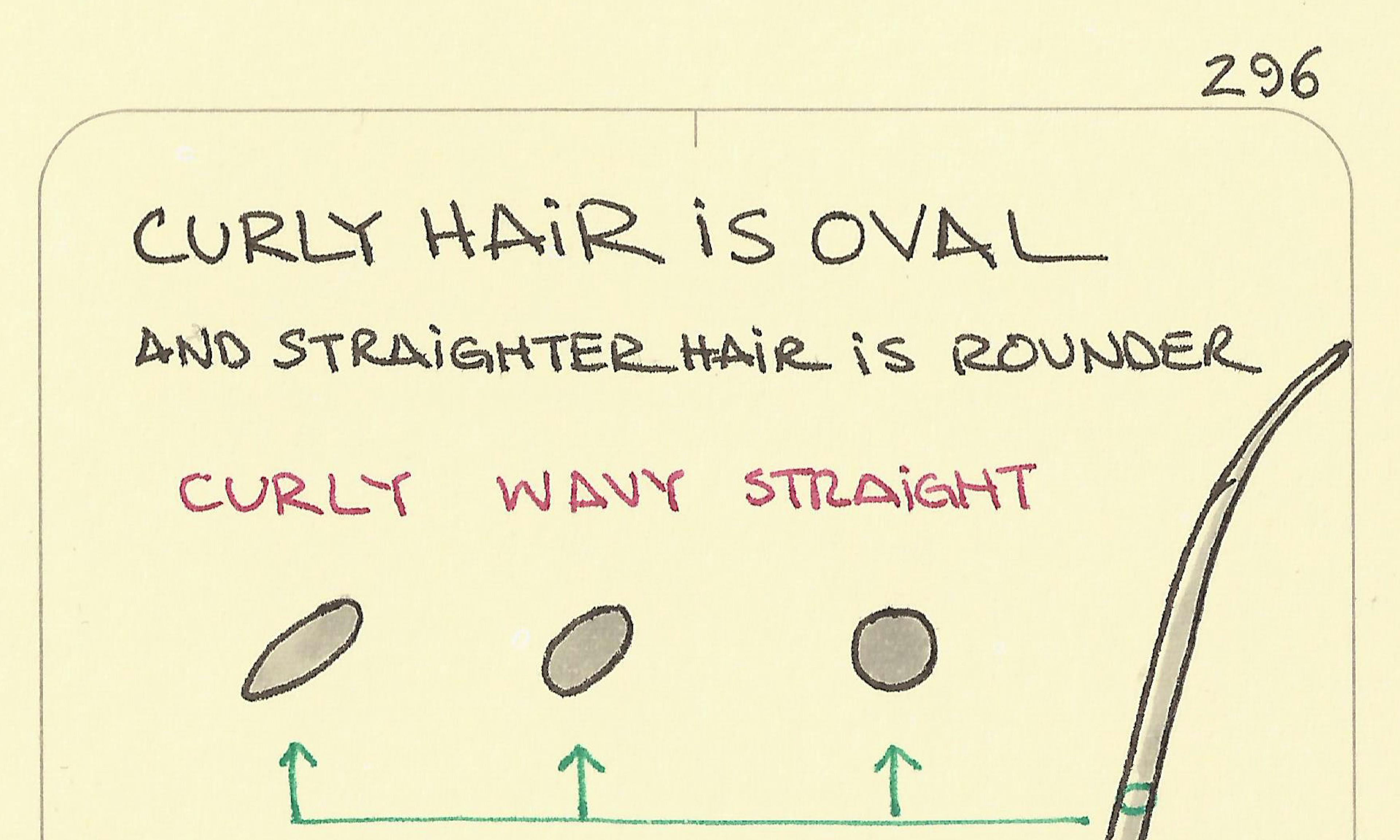 Curly hair is oval
Curly hair is oval Know your clouds: How to identify common cloud types
Know your clouds: How to identify common cloud types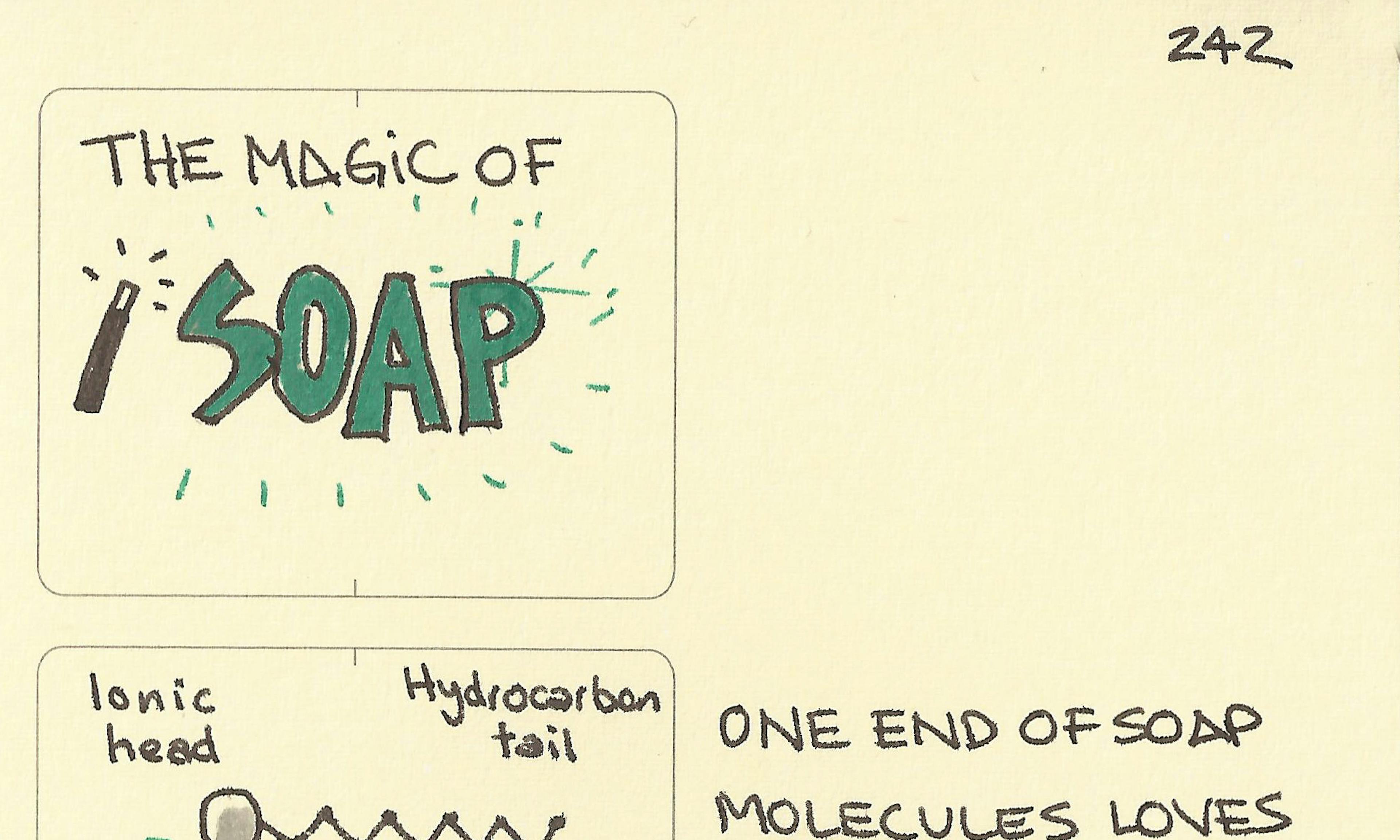 The magic of soap
The magic of soap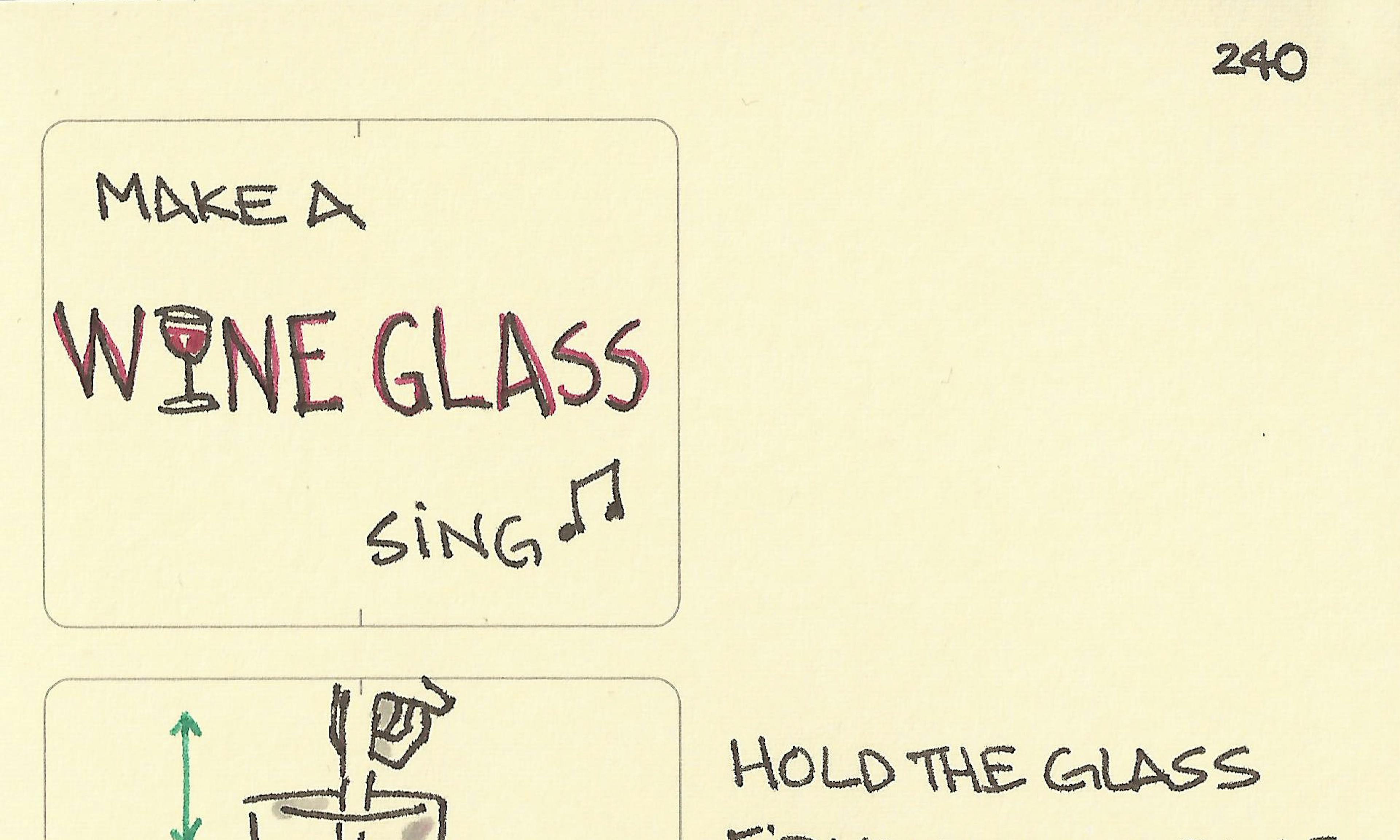 Make a wine glass sing
Make a wine glass sing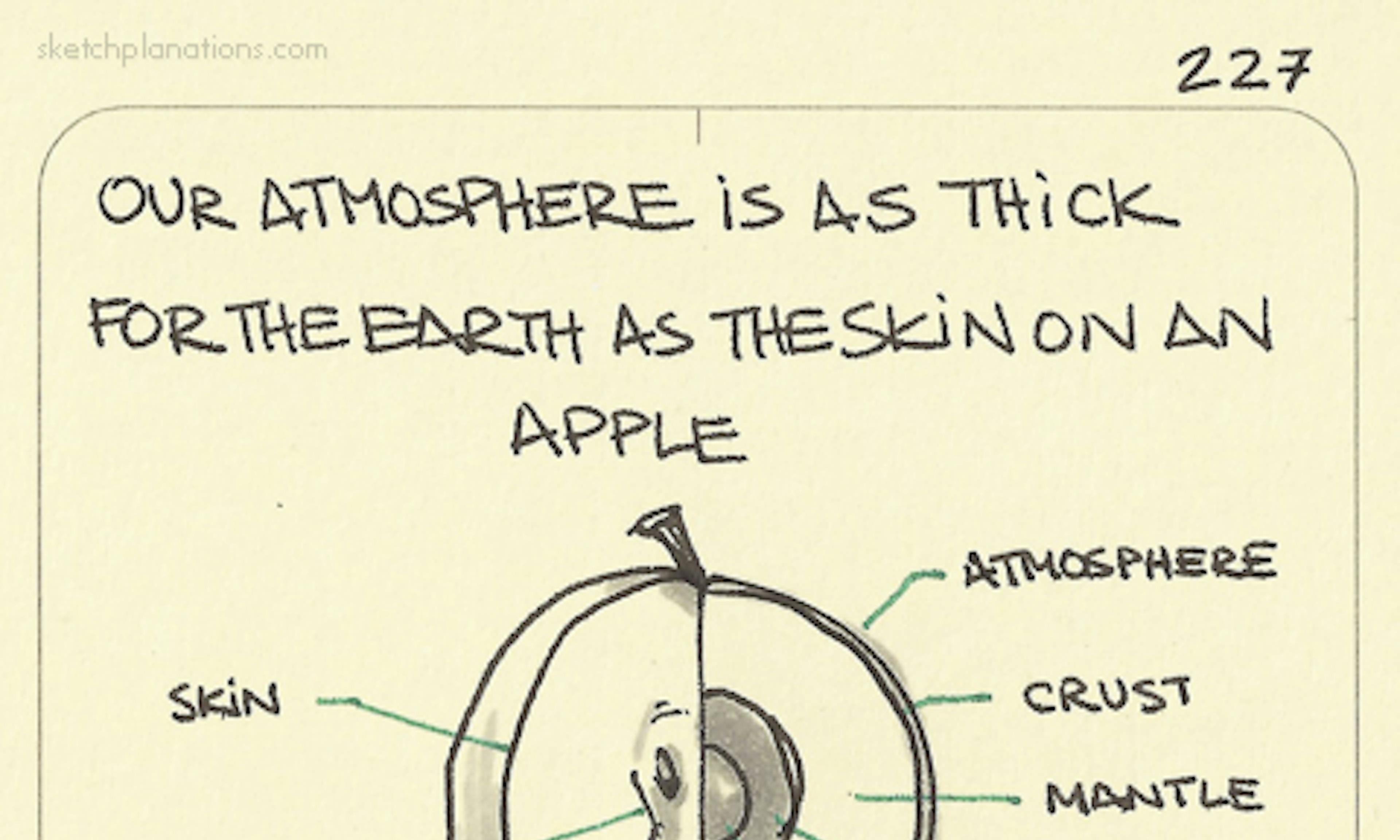 Our atmosphere is as thick for the Earth as the skin on an apple
Our atmosphere is as thick for the Earth as the skin on an apple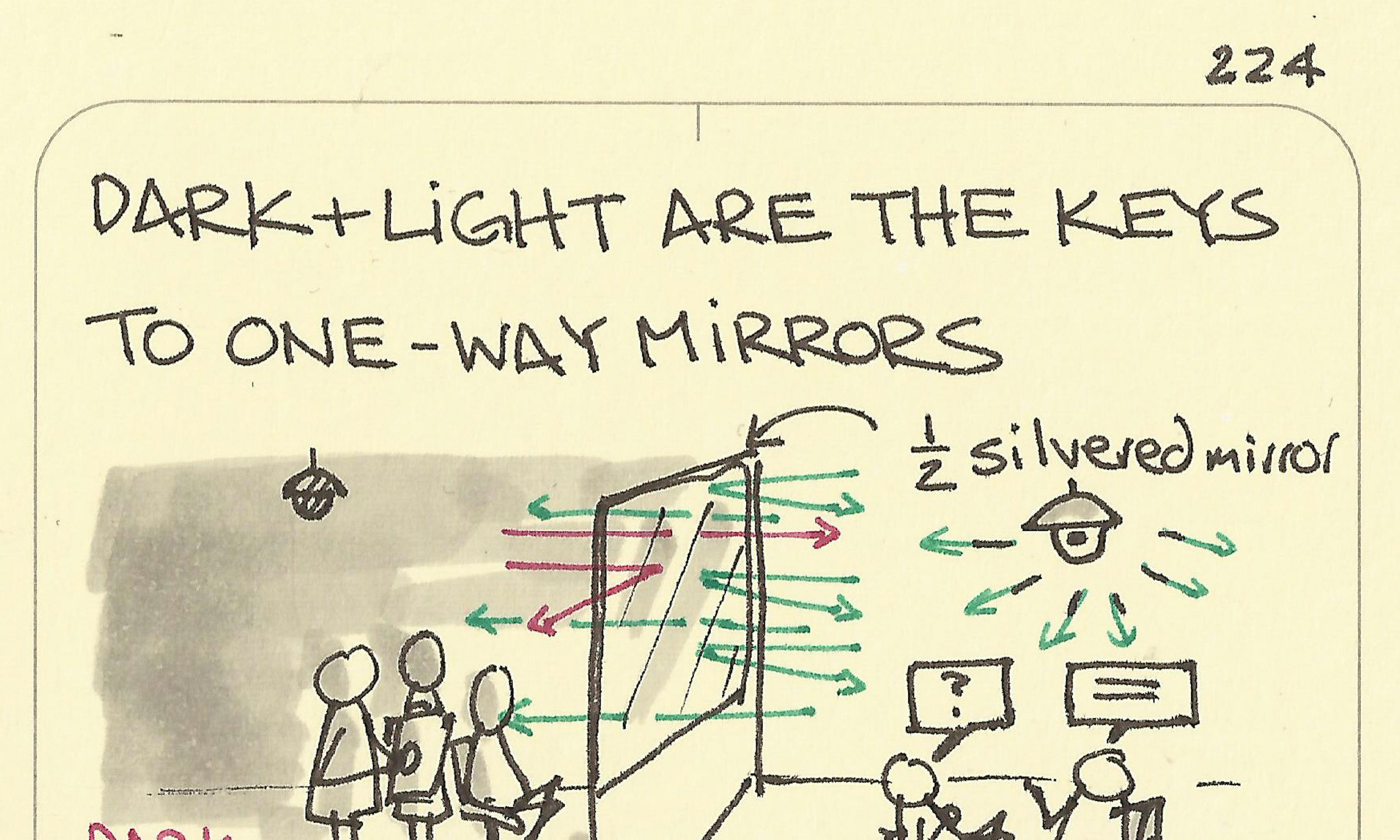 Dark and light are the keys to one-way mirrors
Dark and light are the keys to one-way mirrors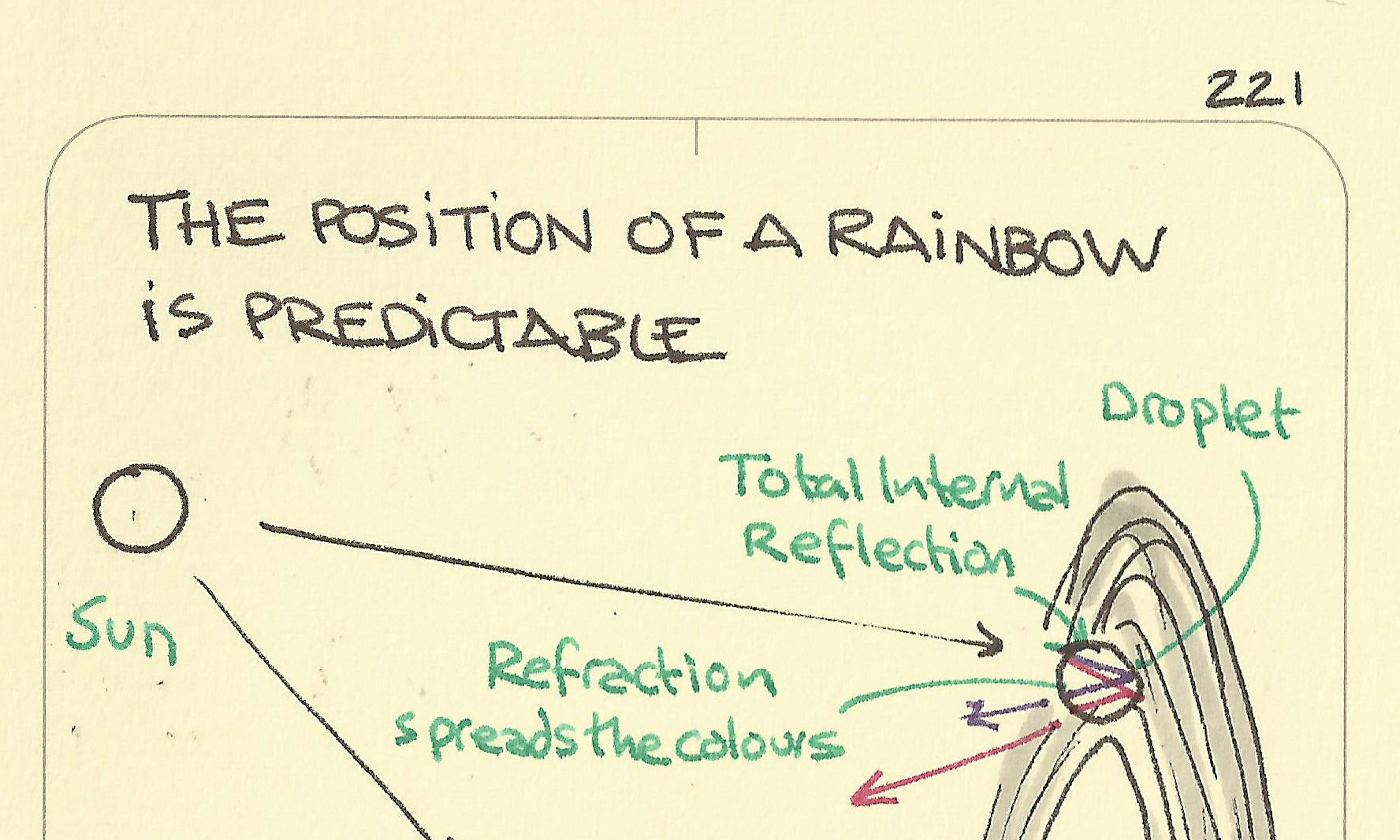 The position of a rainbow is predictable
The position of a rainbow is predictable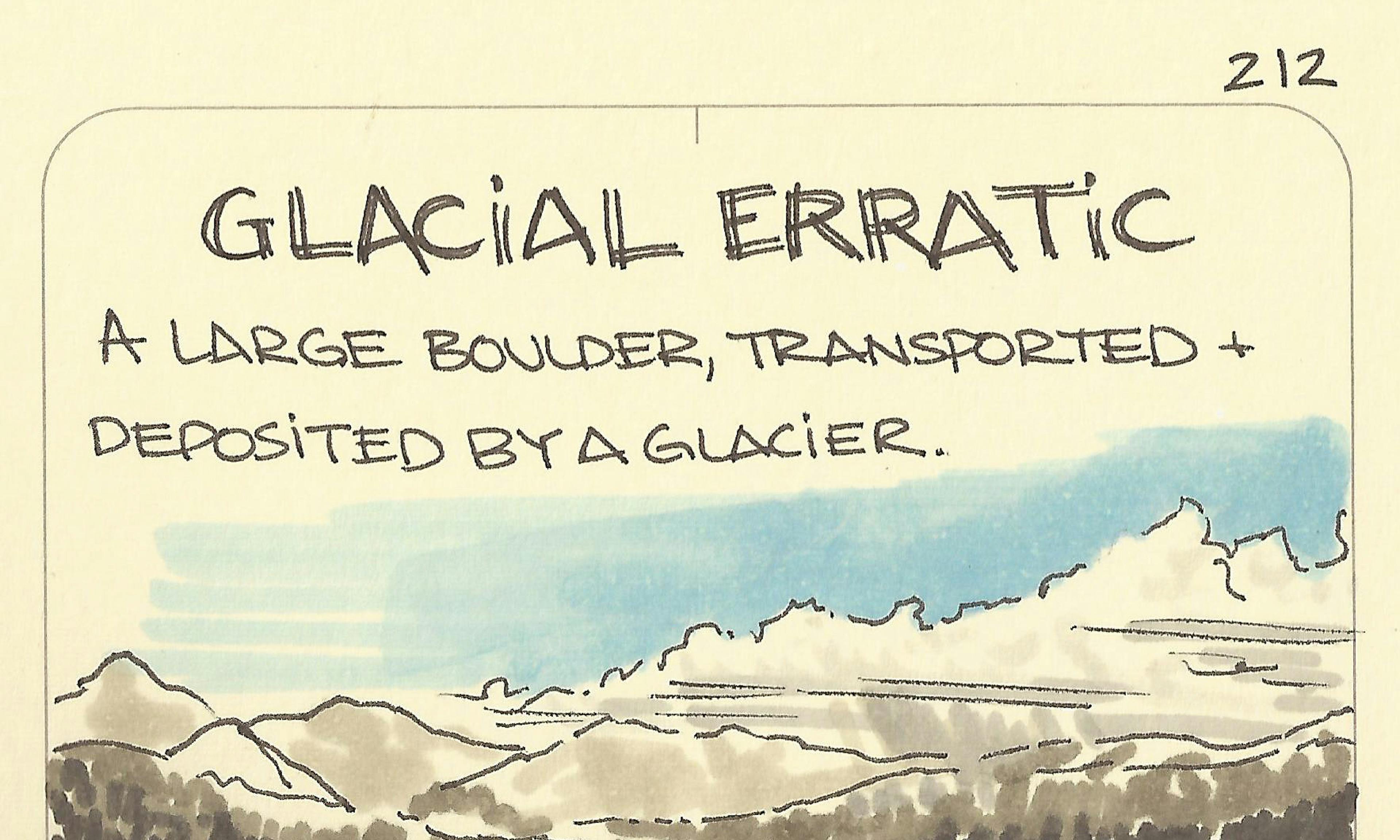 Glacial erratic
Glacial erratic Pollution is highly localized: take the back streets
Pollution is highly localized: take the back streets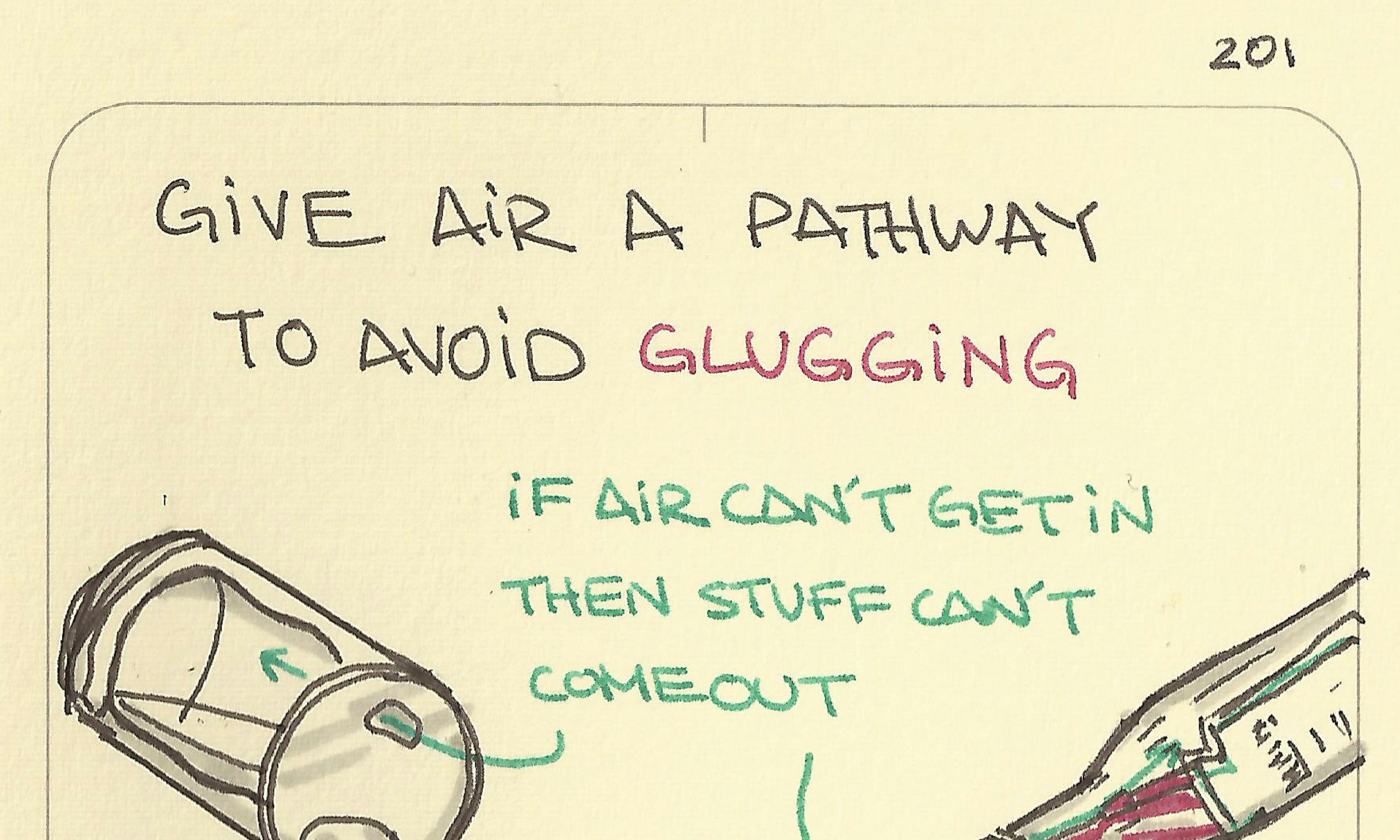 Give air a pathway to avoid glugging
Give air a pathway to avoid glugging Why ice doesn’t sink
Why ice doesn’t sink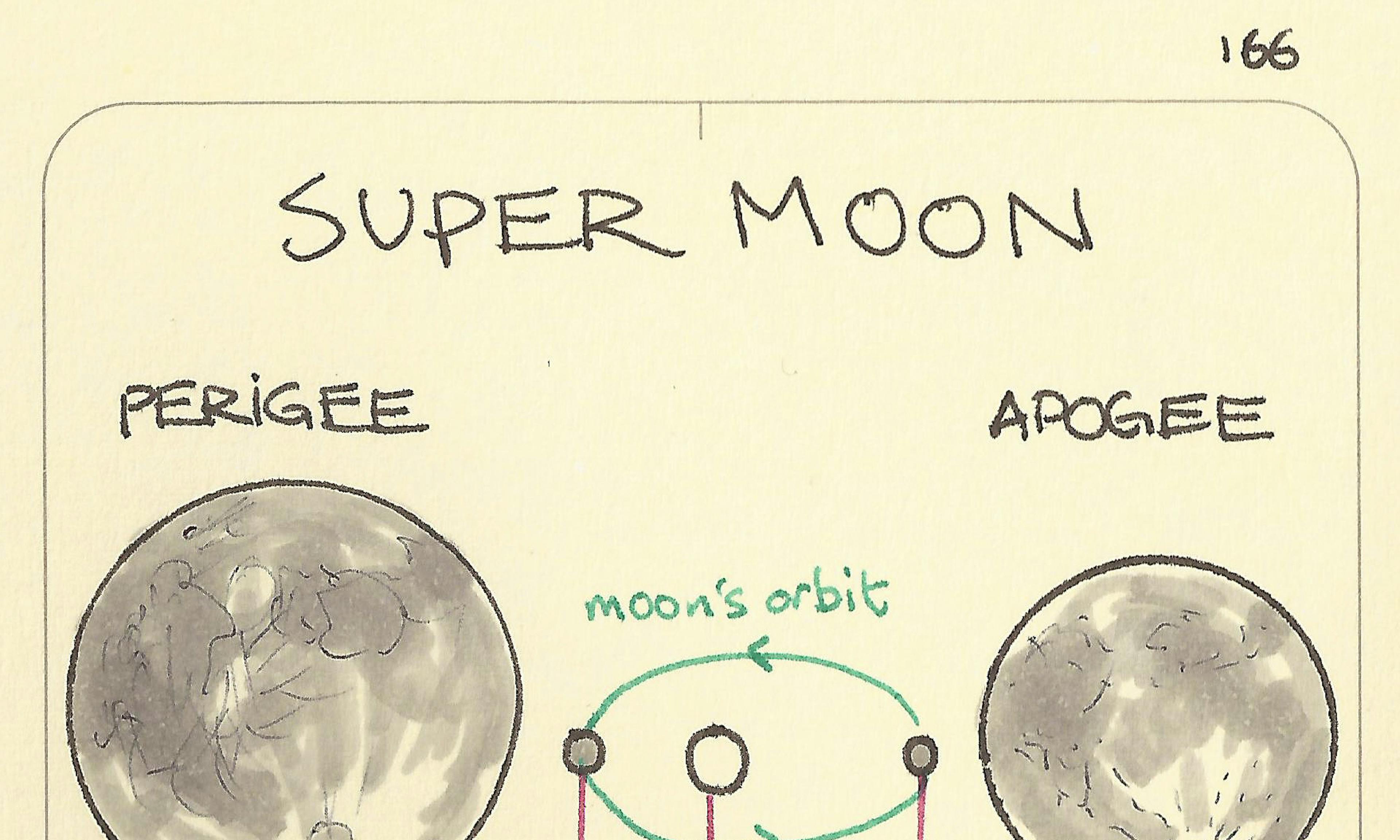 Supermoon
Supermoon More is different
More is different Anatomy of a wave
Anatomy of a wave On microwaves
On microwaves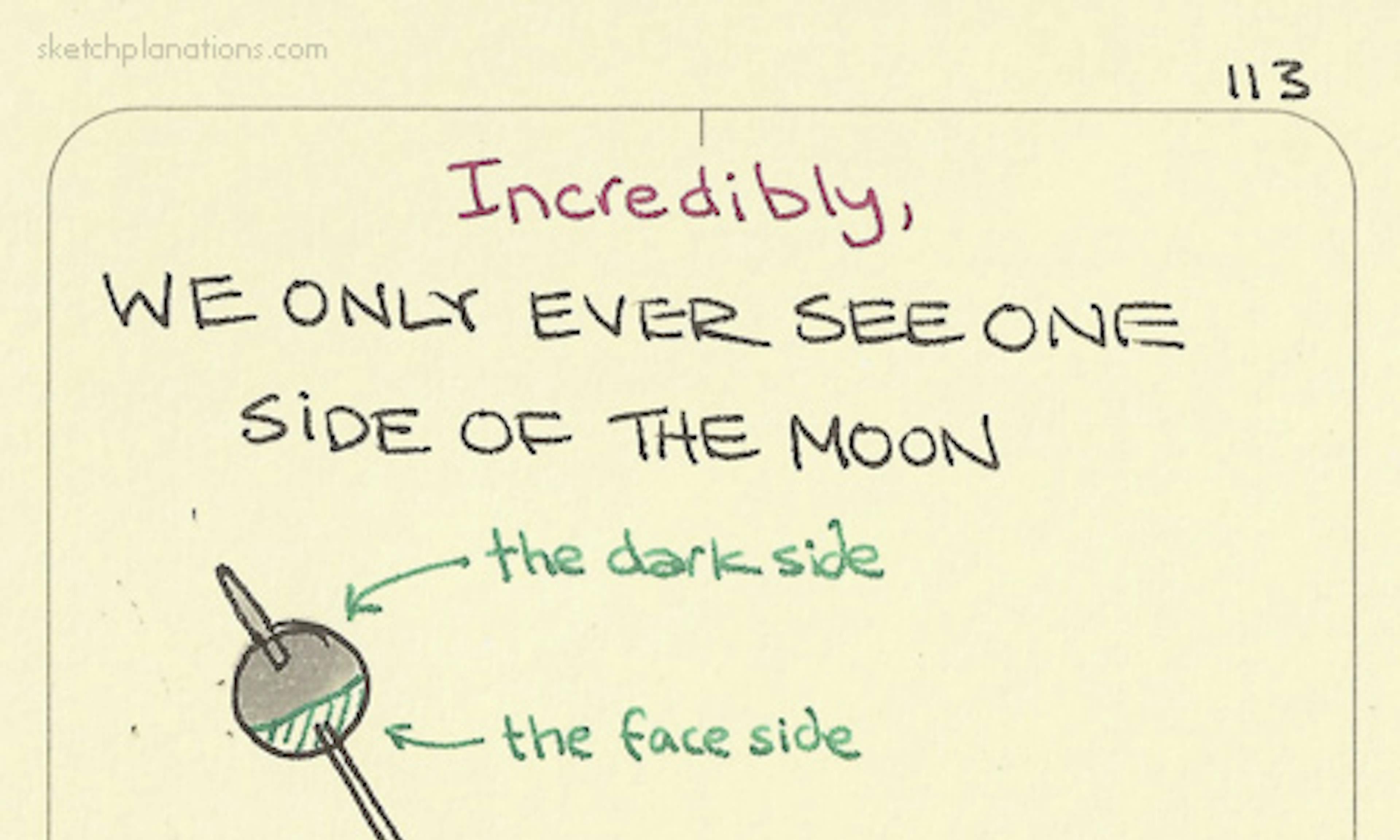 Incredibly, we only ever see one side of the moon
Incredibly, we only ever see one side of the moon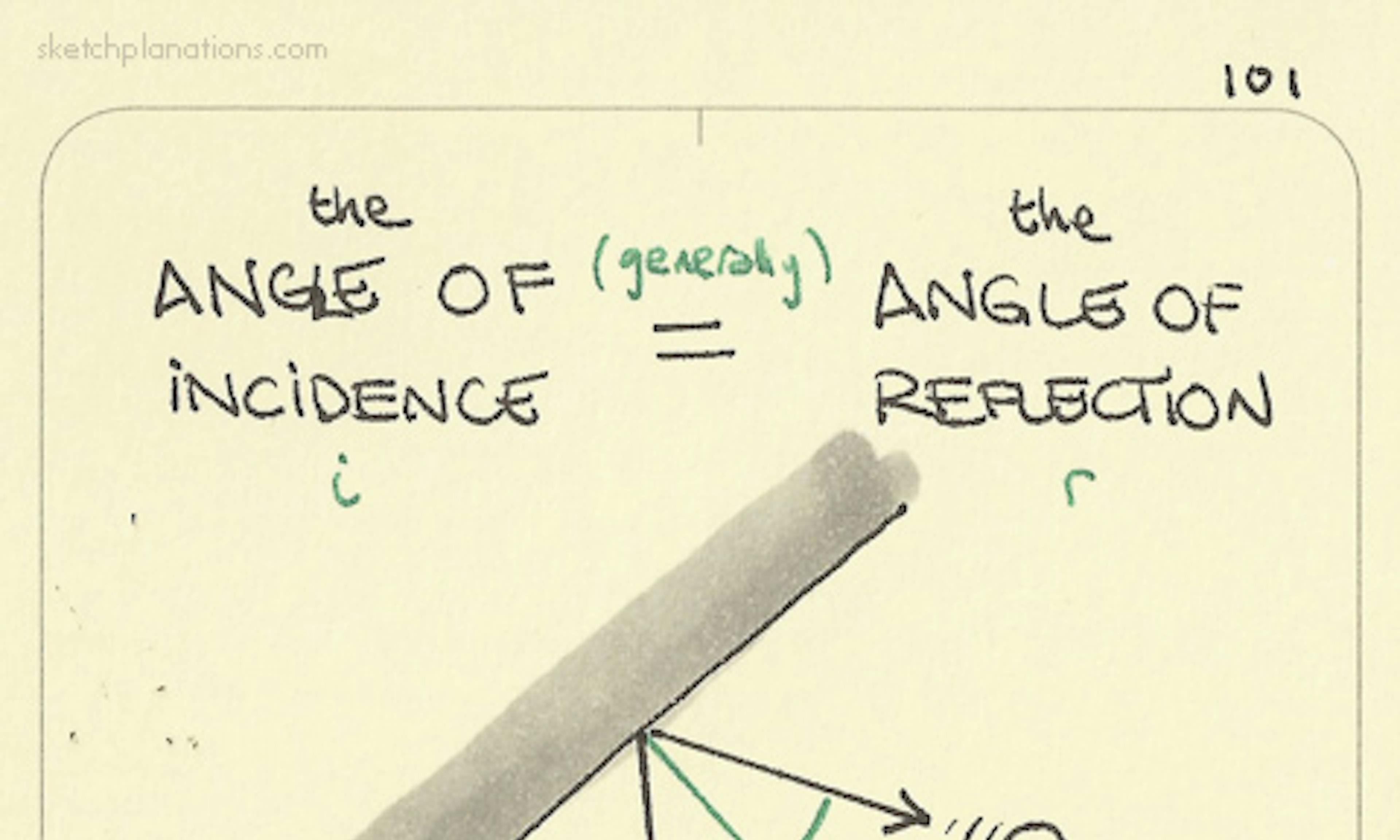 the Angle of Incidence equals the Angle of Reflection
the Angle of Incidence equals the Angle of Reflection Sonar + Echolocation
Sonar + Echolocation
