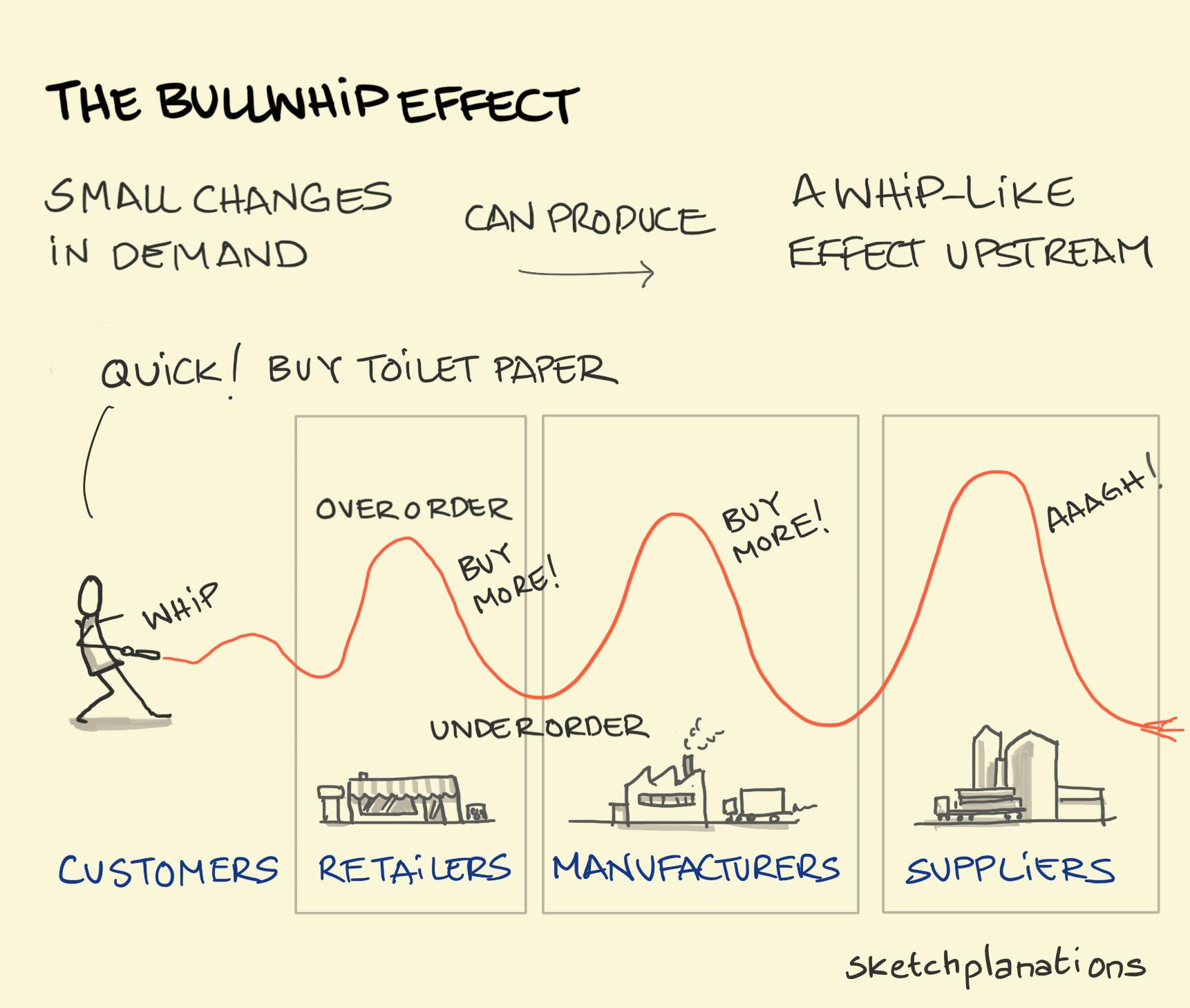
The Bullwhip Effect
- Download
- Copied!
👇 Get new sketches each week
How small changes in customer demand can produce considerable disruption upstream in the supply chain. For instance, a sudden surge in the buying of toilet paper may cause retailers to put in larger orders to make sure they can keep up with demand. Manufacturers, in turn, may put in even larger orders for raw materials to make sure they don’t get caught out. In the meantime, customers had bought all the toilet paper they ever needed and demand suddenly dropped causing retailers to cancel all their orders, manufacturers to halt production and suppliers to be left with big stockpiles of unwanted raw materials.
I learned about the bullwhip effect from Tomas Tunguz where he considers economic effects of the coronavirus. He explains it with a brewery example in his article on proxy metrics for startups .

